Blood Clots And Deep Vein Thrombosis: Prevention And Treatment
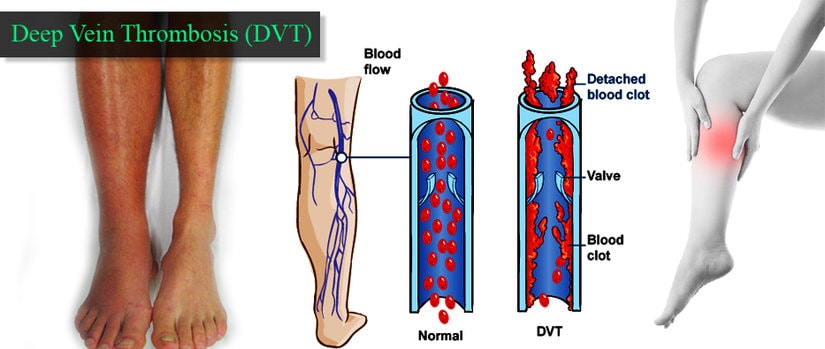
Blood clots and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) are serious medical conditions that can lead to life-threatening complications if not properly treated. Blood clots can form in any part of the body, but DVT occurs specifically in the deep veins of the legs, thighs, or pelvis.
DVT can cause pain, swelling, and warmth in the affected area, and if left untreated, can lead to a pulmonary embolism, which can be fatal.
Risk factors for blood clots and DVT include prolonged immobility, surgery, pregnancy, obesity, and smoking. It is important to understand the risks of blood clots and take proactive measures to prevent their formation.
This article will explore the various prevention and treatment methods available for blood clots and DVT, including lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and compression stockings.
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in preventing complications and ensuring a successful recovery.
Key Takeaways
- Prevention and early detection are critical for reducing the risk of complications associated with blood clots and DVT.
- Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and the use of compression stockings can help reduce the risk of blood clots forming.
- Medical interventions such as anticoagulant therapy and thrombolytic therapy may be necessary to manage blood clots, and surgical interventions may be required in more severe cases.
- Individuals at high risk of developing blood clots can take preventive measures such as using compression stockings and blood thinners, and avoiding prolonged periods of immobility.
Understanding the Risks of Blood Clots
An understanding of the risks associated with blood clots is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies, as these risks are multifactorial and can vary among different populations.
Blood clots can occur in any blood vessel in the body, but they are most commonly seen in the deep veins of the legs, pelvis, and arms. These clots can cause serious health problems, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), and stroke.
There are several factors that can increase the risk of blood clots, including age, obesity, immobility, surgery, pregnancy, certain medications, and genetic factors. In addition, individuals with a history of blood clots or a family history of blood clotting disorders may be at higher risk.
Prevention and early detection are critical for reducing the risk of complications associated with blood clots. Healthcare providers need to be aware of these risk factors and take appropriate measures to prevent blood clots from forming or to treat them promptly if they do occur.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Risk
Implementing lifestyle modifications can be an effective way to decrease the likelihood of developing certain health conditions. In the case of blood clots and deep vein thrombosis (DVT), lifestyle changes can help to reduce the risk of developing these conditions.
One of the most important changes that individuals can make is to adopt a more active lifestyle. Regular exercise can improve blood flow and can reduce the likelihood of blood clots forming. Even moderate exercise, such as walking for 30 minutes a day, can be beneficial.
Another lifestyle change that can help to reduce the risk of blood clots and DVT is to maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight or obese can put additional strain on the circulatory system, increasing the likelihood of blood clots forming. Eating a healthy, balanced diet that is low in saturated fats and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help individuals to maintain a healthy weight and reduce their risk of developing blood clots.
Additionally, it is important to avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption, as both of these activities can increase the risk of blood clots forming.
By making these lifestyle changes, individuals can take proactive steps towards reducing their risk of developing blood clots and DVT.
Medical Treatments for Blood Clots
Medical interventions for managing venous diseases are crucial in preventing life-threatening complications. While lifestyle changes such as regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of developing blood clots, medical treatments are necessary for those who have already developed clots.
There are several medical interventions that can be utilized to manage blood clots and prevent them from causing serious harm. One option for treating blood clots is anticoagulant therapy, which involves the use of blood-thinning medications that prevent the clot from growing larger and decrease the risk of new clots forming.
Another medical intervention is thrombolytic therapy, which involves the use of medications that dissolve blood clots. In more severe cases, surgical interventions such as thrombectomy (surgical removal of the clot) or the insertion of a vena cava filter (a small device that prevents clots from entering the lungs) may be necessary.
It is important to consult with a medical professional to determine the most appropriate course of treatment for each individual case.
Compression Stockings and Other Prevention Methods
Compression stockings and other preventative measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing venous diseases and their associated complications. Compression stockings are specialized garments that apply pressure to the lower legs, ankles, and feet, thereby promoting better blood flow in the veins. The pressure exerted by these stockings helps prevent blood from pooling in the lower extremities and reduces the risk of clot formation.
Compression stockings are commonly recommended for people who are at high risk of developing blood clots, such as those who have had recent surgery or who have a history of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). They are also recommended for people who spend long periods sitting or standing, as these activities can increase the risk of blood clots.
In addition to compression stockings, other preventative measures that can reduce the risk of venous diseases include regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing. Exercise helps promote better blood flow and strengthens the muscles that support the veins. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the pressure on the veins and reduces the risk of developing varicose veins. Avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing can also help reduce the risk of blood clots.
People who have jobs that require them to sit or stand for long periods should take frequent breaks to stretch their legs and move around. Overall, these preventative measures can help reduce the risk of developing venous diseases and can improve overall vascular health.
Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis
One of the most commonly experienced symptoms of DVT is swelling in the affected leg. This occurs because the blood clot restricts the flow of blood in the affected vein, causing blood to pool in the area. The swelling may be accompanied by pain, tenderness, and warmth in the affected area, and the skin may become red or discolored.
In addition to swelling, other symptoms of DVT can include a feeling of heaviness or tightness in the leg, especially when standing or walking. Some people may also experience cramping or aching in the affected area, which can worsen over time.
It’s important to note that not everyone with DVT will experience symptoms, and some people may only have mild symptoms that are easy to overlook. If you suspect that you may have a blood clot, it’s important to seek medical attention right away.
Diagnosing Blood Clots
Diagnosis of a potential blood clot involves utilizing imaging techniques to visualize the affected vein and identify any blockages or abnormalities. The most commonly used imaging techniques are ultrasound, venography, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Ultrasound is the most widely used technique as it is non-invasive, readily available, and cost-effective. It uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the blood vessels and determine the presence of a clot. Venography involves injecting a contrast dye into the blood vessels and taking X-ray images to detect the clot. This technique is more invasive and may cause discomfort to the patient. MRI uses a magnetic field and radio waves to produce detailed images of the blood vessels and is useful in detecting clots in deep veins.
To aid in the diagnosis of blood clots, a clinical prediction score called the Wells score is often used. The Wells score takes into account the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and risk factors for blood clots and assigns a score that indicates the likelihood of having a clot. A score of 2 or higher warrants further testing, such as an ultrasound or D-dimer blood test. The D-dimer blood test measures a protein fragment that is released when a blood clot breaks down. If the D-dimer level is elevated, it may indicate the presence of a blood clot, but further imaging tests are needed to confirm the diagnosis. Utilizing these diagnostic tools, healthcare professionals can accurately diagnose blood clots and establish a treatment plan to prevent complications.
| Diagnostic Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrasound | Non-invasive, readily available, cost-effective | May not detect clots in certain locations | ||||
| Venography | Accurate, can detect clots in deep veins | Invasive, requires contrast dye injection, may cause discomfort | ||||
| MRI | Accurate, can detect clots in deep veins | Expensive, may not be readily available in all healthcare settings | Ultrasound | Non-invasive, can detect clots in both superficial and deep veins | Operator-dependent, may not be as accurate in obese patients or those with heavily calcified vessels |
Complications of Blood Clots
Complications associated with the formation of a thrombus can lead to severe consequences if not promptly treated. One of the most significant complications is the potential for the clot to dislodge and travel through the bloodstream, causing an embolism. An embolism occurs when a blood clot or other foreign material, such as air or fat, travels through the bloodstream and lodges in a blood vessel. When this happens, the embolism can block blood flow to vital organs, leading to serious health consequences such as stroke, heart attack, or pulmonary embolism.
In addition to embolisms, blood clots can also lead to chronic venous insufficiency, a condition in which the veins in the legs are unable to effectively return blood to the heart. This can cause swelling, pain, and skin changes in the affected leg.
Furthermore, blood clots can damage the walls of the affected blood vessels, leading to scarring and narrowing of the vessel, a condition known as post-thrombotic syndrome.
Finally, in rare cases, a blood clot in the deep veins of the legs or pelvis can cause a condition called phlegmasia cerulea dolens, which is characterized by severe swelling and blue discoloration of the affected limb.
In conclusion, the complications associated with blood clots can be severe and debilitating. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent these complications and improve patient outcomes.
Importance of Proactive Health Measures
Proactive health measures play a crucial role in mitigating the potentially devastating consequences of thrombus formation. Blood clots and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can have serious health complications, including pulmonary embolism, stroke, and heart attack.
However, individuals can take various steps to prevent blood clots and reduce the risk of developing DVT. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential in preventing blood clots. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and maintaining a healthy weight are all factors that can help reduce the risk of developing DVT.
Additionally, individuals at high risk of developing blood clots, such as those with a personal or family history of blood clots, can take preventive measures such as using compression stockings, taking blood thinners, and avoiding prolonged periods of immobility.
By taking proactive health measures, individuals can reduce the likelihood of developing blood clots and minimize the risk of serious complications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blood clots and deep vein thrombosis are serious medical conditions that can have life-threatening consequences if left untreated. Understanding the risks associated with blood clots and implementing lifestyle changes to reduce these risks can play a crucial role in preventing blood clots from forming.
Medical treatments such as anticoagulant medications and surgical interventions are available to treat blood clots, but early diagnosis is key to preventing further complications.
Preventative measures such as wearing compression stockings and regular exercise can significantly reduce the risk of developing blood clots. It is important to be aware of the symptoms of deep vein thrombosis and seek medical attention immediately if they are present.
Proactive measures such as maintaining a healthy weight, not smoking, and managing chronic conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure can also play a significant role in preventing blood clots. By taking a proactive approach to health and understanding the risks associated with blood clots, individuals can take control of their health and reduce the risk of developing serious medical conditions.