Bone Structure And Functions
Bone structure and its functions are essential components that contribute to the overall health of the human body. Bones are the structural framework that provides support to the body, protects vital organs, and acts as a mineral storehouse. Understanding the composition and function of bones is crucial to maintaining optimal health and preventing various diseases such as osteoporosis, fractures, and joint pains.
The human body consists of 206 bones, classified into five categories based on their shape and function. Long bones, such as the femur and humerus, support body weight and facilitate movement. Short bones, such as those found in the wrist and ankle, provide stability and support. Flat bones, such as the skull, ribcage, and shoulder blades, protect the vital organs. Irregular bones, such as the vertebrae and facial bones, have complex shapes and perform various functions. Sesamoid bones, such as the patella or kneecap, are small bones embedded in tendons that protect the joints and enhance their function.
Understanding the different types of bones and their functions is essential to maintaining a healthy body.
Key Takeaways
- Bones provide support, protect vital organs, and store minerals.
- The skeletal system is made up of bones, cartilage, and connective tissue.
- Maintaining bone health is crucial for overall health and preventing diseases.
- Regular exercise, adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, and avoiding unhealthy habits can help maintain strong and healthy bones.
Types of Bones in the Human Body
The human body is composed of five types of bones, including long bones, short bones, flat bones, irregular bones, and sesamoid bones.
Long bones, such as the femur and humerus, are longer than they are wide and are found in the limbs.
Short bones, such as the carpals and tarsals, are roughly equal in length and width and are found in the wrist and ankle.
Flat bones, such as the scapula and sternum, are thin, flat, and curved bones that protect internal organs and provide attachment points for muscles.
Irregular bones, such as the vertebrae and facial bones, have complex shapes that do not fit into any of the other categories.
Sesamoid bones, such as the patella, are small bones embedded within tendons that protect them from wear and tear and increase the mechanical advantage of the muscle.
Each type of bone in the human body serves a specific function. Long bones provide support and facilitate movement, while short bones provide stability and support. Flat bones protect internal organs and provide attachment points for muscles, while irregular bones protect the spinal cord and provide attachment points for muscles of the back. Sesamoid bones protect tendons and improve their mechanical advantage.
Understanding the different types of bones and their functions is essential for maintaining healthy bones and preventing bone injuries and diseases.
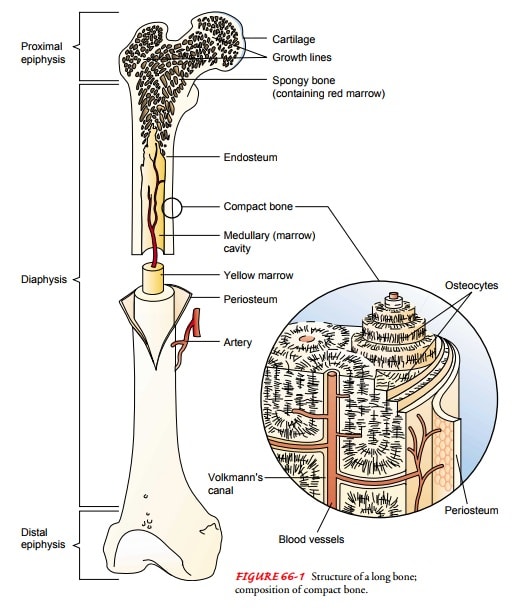
Composition of Bones: Bone, Cartilage, and Connective Tissue
Comprising of different types of tissues, the skeletal system is responsible for providing support, protection, and movement to the body. Bones, cartilage, and connective tissue are the three primary components that make up the skeletal system. Bones, which are the primary structural component of the skeletal system, are highly mineralized and rigid, providing strength and support to the body. In addition, bones also act as a storage site for minerals such as calcium and phosphorus, which are essential for various physiological functions.
Cartilage, on the other hand, is a flexible and elastic connective tissue that provides cushioning and support to the joints. It is found in various parts of the body such as the nose, ears, and ribcage. Although it is not as strong as bone, cartilage is highly resistant to compression forces, making it ideal for areas that require flexibility and shock absorption. Lastly, connective tissue provides structural support to the skeletal system by holding the bones together and facilitating joint movement. It is composed of various types of fibrous proteins such as collagen, elastin, and reticular fibers, which provide strength and durability to the skeletal system.
To add depth to this section, a table can be included to summarize the different components of the skeletal system. The table should have three columns and four rows, with the first column listing the three primary components of the skeletal system, and the second and third columns detailing their respective characteristics. This table can serve as a useful resource for those seeking a quick overview of the skeletal system’s composition.
Function of Bones in Supporting the Body’s Weight
One of the key roles of the skeletal system is to provide a framework that supports the weight of the body, allowing for upright posture and movement. The bones in the body act as levers, which are pulled by muscles to enable movement. Without the support of the skeletal system, the body would not be able to stand, walk, run, or perform any other physical activities.
Bones also play an essential role in protecting vital organs such as the brain, heart, and lungs. The skull, rib cage, and spine are all examples of bones that provide protection to these organs.
Moreover, bones act as a storage site for minerals such as calcium and phosphorus, which are necessary for various physiological processes in the body.
In conclusion, the skeletal system is an essential component of the human body, and its primary function is to provide structural support and protection to the body’s vital organs.
Protection of Vital Organs
Vital organs such as the brain, heart, and lungs are shielded from damage by the skeletal system. The bones of the skull encase and protect the brain, while the ribcage and sternum provide a protective shield for the heart and lungs. The spinal column, composed of vertebrae, surrounds and protects the spinal cord. Without the skeletal system, these vital organs would be left vulnerable to injury and trauma.
In addition to providing physical protection, the skeletal system also plays a role in the protection of vital organs from disease and infection. Bone marrow, found in the center of bones, is responsible for the production of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These blood cells are essential for the immune system’s ability to fight off infections and diseases. Without the skeletal system’s contribution to the production of these cells, the body would be left vulnerable to a variety of illnesses.
Therefore, the skeletal system’s function in the protection of vital organs extends beyond just physical protection but also includes the maintenance of overall health and well-being.
Storehouse for Minerals: Calcium and Phosphorus
The skeletal system serves as a significant source of minerals, particularly calcium and phosphorus, that are crucial for maintaining optimal health and physiological functions. The bones act as a storehouse for these minerals, releasing them into the bloodstream as needed.
Calcium is essential for muscle contraction, nerve transmission, blood clotting, and bone health, while phosphorus is necessary for energy production, DNA synthesis, and bone mineralization.
The body maintains a delicate balance of calcium and phosphorus in the bloodstream, and if levels become too low, the bones release more of these minerals to replenish them. Conversely, if levels become too high, the excess is stored within the bones.
Therefore, maintaining healthy bone mass is vital to ensuring adequate levels of calcium and phosphorus in the body. Adequate intake of these minerals through diet or supplements is also crucial for maintaining healthy bones and preventing conditions such as osteoporosis.
Importance of Bone Health
Maintaining optimal levels of calcium and phosphorus in the body is essential for a range of physiological processes, including bone health. Bones are the primary storehouse for these minerals, and they play a critical role in maintaining the balance of these minerals in the body.
Calcium and phosphorus are necessary for the formation, growth, and maintenance of bones. They are responsible for giving bones their hardness and strength, and they also help in repairing damaged bones. Furthermore, these minerals are also important for the proper functioning of other organs, including the heart, kidney, and muscles.
The importance of bone health cannot be overstated. As we age, our bones become weaker, and the risk of fractures and osteoporosis increases. Poor bone health can also contribute to other health problems such as back pain, poor posture, and decreased mobility.
Therefore, it is crucial to maintain optimal bone health throughout our lives. This can be achieved through a balanced diet that includes adequate amounts of calcium and phosphorus, regular exercise, and avoiding unhealthy habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
By taking care of our bones, we can enjoy a healthier and more active life.
Ways to Keep Your Bones Strong and Healthy
Maintaining good bone health is crucial in preventing various diseases, especially as we age. In the previous subtopic, we discussed the importance of bone health and why it should not be taken for granted. In this subtopic, we will delve deeper into the practical ways we can keep our bones strong and healthy.
- Regular exercise: Engaging in weight-bearing activities such as jogging, dancing, and lifting weights helps to strengthen your bones and keep them healthy.
- Adequate calcium and vitamin D intake: Calcium and vitamin D are essential for bone health. Eating calcium-rich foods such as dairy products and leafy greens and getting enough vitamin D from sunlight or supplements can help keep your bones strong.
- Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can weaken bones, so it’s crucial to limit or eliminate these habits for good bone health.
- Regular bone density tests: Bone density tests can help detect bone loss and osteoporosis early, allowing for prompt treatment and prevention of further bone loss.
Taking steps to keep your bones healthy is essential for overall health and well-being. Incorporating these simple but effective ways into your lifestyle can go a long way in maintaining strong and healthy bones.
Conclusion
The human body is comprised of various types of bones that play an important role in supporting the body’s weight, protecting vital organs, and storing minerals such as calcium and phosphorus.
Bones are composed of bone, cartilage, and connective tissue, which work together to provide structure and strength.
The health of our bones is essential for overall wellness, as they not only support the body but also aid in movement and protect against injury.
It is important to maintain strong and healthy bones throughout our lives.
This can be achieved through a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, regular exercise, and avoiding unhealthy habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
By taking care of our bones, we can prevent conditions such as osteoporosis and fractures, and improve our overall quality of life.
In conclusion, understanding the types and functions of bones in the human body can help us appreciate the importance of bone health and take proactive steps to maintain it.