Hemophilia: Living With A Genetic Blood Disorder
Hemophilia is a rare genetic disorder that affects the blood’s ability to clot properly. It is caused by a deficiency in clotting factors, which are proteins that help the blood to clot and stop bleeding.
Hemophilia is an inherited disorder that is passed down from parents to children through the genes.
Living with hemophilia can be challenging, as it can lead to excessive bleeding and bruising, and can cause joint pain and swelling.
Treatment options for hemophilia include medications and therapies that can help to control bleeding and prevent complications.
Coping with hemophilia also involves making lifestyle changes and finding support from healthcare providers, family, and community resources.
This article will provide an overview of hemophilia, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and the emotional challenges that come with living with this condition.
Key Takeaways
- Hemophilia is a rare genetic disorder caused by a deficiency in clotting factors, and it can cause excessive bleeding, bruising, joint pain, and swelling.
- Treatment options include medications and therapies to control bleeding and prevent complications, and there are two main types of hemophilia: A and B, caused by deficiencies in clotting factors VIII and IX, respectively.
- Coping with hemophilia requires significant lifestyle changes and support from healthcare professionals and community resources, and individuals with hemophilia may experience anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues.
- Hemophilia can lead to joint damage, chronic pain, and other complications if left untreated or improperly managed, but it can be managed through a multidisciplinary approach that involves medical care, physical therapy, and counseling.
Understanding Hemophilia: Causes and Symptoms
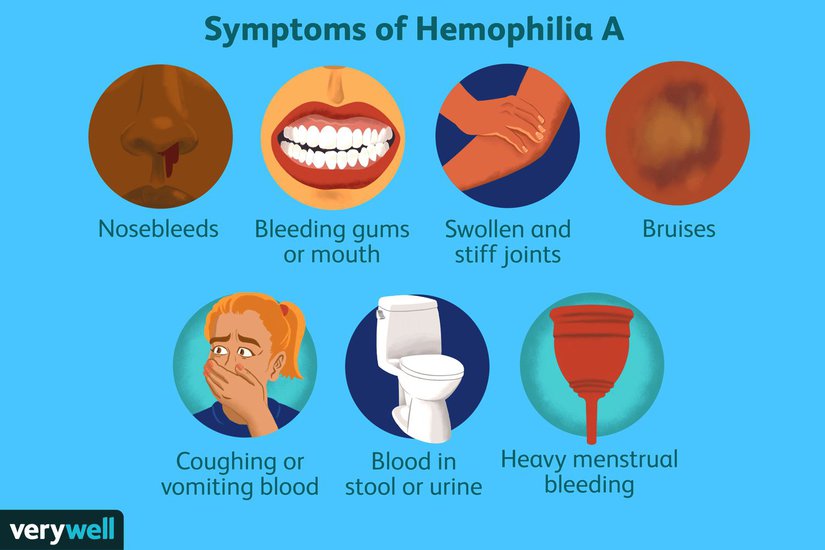
The etiology of hemophilia involves a genetic mutation that affects the clotting factors in the blood, resulting in excessive bleeding and bruising, which are the hallmark symptoms of this disorder.
Hemophilia is caused by a deficiency or absence of specific clotting factors in the blood, which are responsible for stopping bleeding after an injury.
There are two main types of hemophilia: hemophilia A, caused by a deficiency of clotting factor VIII, and hemophilia B, caused by a deficiency of clotting factor IX.
Hemophilia is a sex-linked genetic disorder, which means that it is more common in males than females because the gene for hemophilia is located on the X chromosome.
The severity of hemophilia varies depending on the degree of clotting factor deficiency.
Individuals with severe hemophilia have less than 1% of normal clotting factor levels and are at high risk for spontaneous bleeding into their joints, muscles, and organs.
People with mild or moderate hemophilia have higher levels of clotting factors and may only experience bleeding after an injury or surgery.
Hemophilia is diagnosed through a blood test that measures the level of clotting factors in the blood.
Treatment for hemophilia includes replacement therapy with clotting factor concentrates, which are infused into the bloodstream to replace the missing clotting factors and prevent bleeding.
Diagnosing Hemophilia: Tests and Procedures
Tests and procedures used to diagnose hemophilia involve assessing the levels and activity of clotting factors in the blood. Here are some of the most commonly used methods for diagnosing this condition:
- Clotting factor tests: These tests measure the levels of clotting factors in the blood. A doctor may order several different clotting factor tests to determine which factor is deficient in the patients blood.
- Bleeding time test: In this test, a small cut is made on the patients skin, and the amount of time it takes for the bleeding to stop is measured. People with hemophilia have longer bleeding times than those without the condition.
- Genetic testing: This involves analyzing a patients DNA to determine whether they have a genetic mutation that causes hemophilia. Genetic testing is especially useful for women who carry the gene for hemophilia but do not show any symptoms themselves.
- Mixing studies: In this test, a sample of the patients blood is mixed with a sample of blood that contains normal clotting factors. If the patients blood is unable to form a clot even after being mixed with normal blood, this suggests that they have a clotting factor deficiency.
- Factor activity tests: These tests measure the activity of specific clotting factors in the blood. They can help determine the severity and type of hemophilia a patient has.
Diagnosing hemophilia requires a combination of these tests and procedures. In some cases, a doctor may need to perform additional tests to rule out other conditions that can cause bleeding disorders.
Early diagnosis is important for managing hemophilia and preventing serious complications such as joint damage and internal bleeding.
Hemophilia Treatment Options: Medications and Therapies
Various medication and therapy options are available to manage the symptoms of hemophilia and improve the quality of life for those affected. The main goal of treatment is to prevent bleeding or stop bleeding as soon as possible when it occurs. Replacement therapy with clotting factor concentrates is the most common treatment option for hemophilia. There are two types of clotting factor concentrates: plasma-derived and recombinant. Plasma-derived products are made from human blood, while recombinant products are genetically engineered in a laboratory using DNA technology. Both types of products work effectively to replace the deficient clotting factor in hemophilia patients.
Another medication option is desmopressin acetate, which is a synthetic hormone that can stimulate the release of von Willebrand factor and clotting factor VIII from the patient’s own body. This treatment option is only effective in individuals with mild hemophilia A and von Willebrand disease. In addition to medication, physiotherapy and occupational therapy can also be beneficial for hemophilia patients. They can help improve joint mobility, muscle strength, and coordination, which can reduce the risk of joint damage and improve overall physical function. A balanced diet and regular exercise are also important for hemophilia patients to maintain good health and prevent complications.
| Medication/Therapy | Description | Effectiveness | Side Effects | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clotting factor concentrates | Replaces deficient clotting factor in patients | Highly effective | In rare cases, allergic reactions or the development of inhibitors to the treatment | |||||
| Desmopressin acetate | Stimulates the patient’s own clotting factor production | Effective in mild hemophilia A and von Willebrand disease | Headache, nausea, and in rare cases, fluid retention and seizures | |||||
| Physiotherapy/Occupational Therapy | Helps improve joint mobility, muscle strength, and coordination | Effective in reducing joint damage and improving physical function | None | |||||
| Balanced diet and regular exercise | Important for maintaining good health and preventing complications | Effective in preventing complications | None | It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise or diet regimen | They can provide personalized recommendations and ensure safety | Effective in preventing injury and ensuring optimal health outcomes | None |
Coping with Hemophilia: Lifestyle Changes and Support
Coping with the challenges of managing hemophilia requires individuals to make significant lifestyle changes and seek out support from healthcare professionals and community resources.
One of the most important lifestyle changes is to avoid activities that could cause bleeding, such as contact sports and heavy lifting. It is also important to maintain a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and get enough rest to help prevent bleeding episodes. Additionally, individuals with hemophilia may need to take additional precautions, such as wearing protective gear when participating in activities or avoiding certain medications that can increase the risk of bleeding.
In addition to lifestyle changes, seeking out support from healthcare professionals and community resources can help individuals with hemophilia cope with the challenges of the disorder.
Healthcare professionals such as hematologists, nurses, and physical therapists can provide medical care and advice on managing the condition. Community resources such as advocacy groups and support groups can provide emotional support and connect individuals with hemophilia to others who understand their experiences.
With the right lifestyle changes and support, individuals with hemophilia can lead fulfilling and healthy lives.
Hemophilia and Mental Health: Coping with Emotional Challenges
Individuals with bleeding disorders may experience psychological distress due to the impact of their condition on daily life and the uncertainty of future health outcomes. Hemophilia, a genetic blood disorder, can cause frequent and uncontrollable bleeding, which can lead to pain, joint damage, and disability. Coping with such challenges can be emotionally draining, and it is not uncommon for individuals with hemophilia to experience anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues.
To manage the emotional challenges associated with hemophilia, individuals can seek support from mental health professionals, support groups, and their healthcare team. Here are some tips that can help individuals with hemophilia cope with emotional distress:
- Create a strong support system: Having a supportive network of family, friends, and healthcare professionals can help individuals with hemophilia feel more connected and less isolated. They can provide emotional support and help with daily activities, which can reduce stress levels.
- Practice stress-reduction techniques: Activities such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help individuals with hemophilia manage stress and anxiety. These techniques can also help improve sleep quality, which can have a positive impact on mental health.
- Stay informed: Being knowledgeable about hemophilia and its treatments can help individuals with the condition feel more empowered and in control. They can learn about their condition through educational resources, support groups, and their healthcare team. This can help them better understand their treatment options and make more informed decisions about their care.
Navigating intimacy and family life can pose unique challenges for individuals with bleeding disorders such as hemophilia. Hemophilia is a genetic disorder that affects the body’s ability to clot blood, leading to prolonged bleeding and bruising. This can result in physical limitations that can affect an individual’s ability to engage in intimacy and other aspects of family life. Hemophilia can also lead to emotional challenges that can impact relationships with partners and family members.
One of the main challenges that individuals with hemophilia face when it comes to intimacy is the risk of bleeding. Any physical activity that could potentially lead to injury or bruising can be risky for individuals with hemophilia. This can make it difficult to engage in sexual activity or even simple physical affection. Additionally, hemophilia can lead to chronic pain and discomfort, which can also affect an individual’s ability to engage in intimacy. When it comes to family life, individuals with hemophilia may face challenges related to infertility or the risks involved in pregnancy and childbirth. It is important for individuals with hemophilia and their partners to communicate openly about these challenges and work together to find ways to navigate them.
| Challenges | Coping Strategies |
|---|---|
| Risk of bleeding during intimacy | Engage in low-risk activities that minimize the risk of injury, communicate openly with partner about concerns |
| Chronic pain and discomfort | Manage pain through medication and physical therapy, explore alternative forms of intimacy |
| Infertility or risks during pregnancy and childbirth | Consider adoption or surrogacy, work closely with medical professionals to manage risks during pregnancy and childbirth |
The table above provides a summary of some of the challenges that individuals with hemophilia may face when it comes to intimacy and family life, as well as some coping strategies that can help navigate these challenges. It is important for individuals with hemophilia and their partners to work together to find ways to maintain intimacy and build a fulfilling family life despite the challenges posed by this genetic disorder. With the right support and resources, it is possible to overcome these challenges and lead a fulfilling life.
Hemophilia Research and Advancements: Current Developments
Transitioning from the previous subtopic of Hemophilia and Relationships, it is important to recognize the proactive measures being taken to improve the quality of life for those living with this genetic blood disorder. Hemophilia research and advancements have made significant progress in recent years, offering hope for a brighter future for those affected by the condition.
One area of research that has shown promise is gene therapy. This involves the introduction of a healthy gene into the body to replace the defective one responsible for causing hemophilia. While still in the experimental stages, the results have been encouraging, with some patients experiencing significant improvements in clotting factor activity.
Additionally, there have been advancements in the development of extended half-life clotting factor concentrates, which can reduce the frequency of infusions required for patients and lead to a better quality of life.
- Gene therapy:
- Introduction of healthy gene to replace defective one
- Still in experimental stages, but promising results
- Extended half-life clotting factor concentrates:
- Can reduce frequency of infusions required for patients
- Leads to a better quality of life for those living with hemophilia.
Overall, while there is still much to be done in terms of hemophilia research and advancements, the progress made thus far is encouraging. These developments offer hope for a future where individuals with hemophilia can live full, healthy lives free from the limitations and complications that the condition can bring.
Advocacy and Support: Finding Resources and Community for Hemophilia
Accessing support and resources for those impacted by a certain medical condition is crucial for improving their quality of life and overall well-being. This is particularly true for individuals living with hemophilia, a genetic blood disorder that affects the body’s ability to form blood clots. Hemophilia can lead to bleeding episodes that are difficult to control, which can cause joint damage, chronic pain, and other complications. However, with proper treatment and support, individuals with hemophilia can lead full and productive lives.
There are many resources available to individuals with hemophilia and their families, including advocacy organizations, support groups, and medical professionals. Advocacy organizations such as the National Hemophilia Foundation and the Hemophilia Federation of America work to raise awareness about hemophilia, provide education and support, and advocate for policies that benefit the hemophilia community.
Support groups offer a chance for individuals with hemophilia and their families to connect with others who are facing similar challenges, share information and resources, and provide emotional support. Medical professionals such as hematologists and physical therapists are also important resources for individuals with hemophilia, providing medical care and guidance on managing the condition.
By accessing these resources, individuals with hemophilia can find the support they need to manage their condition and improve their quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, living with hemophilia can be challenging, but with proper treatment and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Understanding the causes and symptoms of hemophilia is crucial for early diagnosis and appropriate management. Medical professionals use various tests and procedures to diagnose hemophilia, and treatment options include medications and therapies. Lifestyle changes and emotional support are also essential components of coping with hemophilia.
Furthermore, individuals with hemophilia may face unique challenges in their relationships, including navigating intimacy and family life. However, with advocacy and support, resources and communities are available to help individuals with hemophilia and their families. Ongoing research and advancements in treatment options provide hope for the future.
Overall, with proper management and support, individuals with hemophilia can live full and meaningful lives.