How To Recognize Hypertensive Crisis And Seek Immediate Help?

Hypertensive crisis is a severe medical condition characterized by a sudden and dangerous increase in blood pressure. It is a critical situation that requires immediate medical attention to prevent potential complications and organ damage.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of hypertensive crisis, including its signs and symptoms, the importance of seeking immediate medical help, and the risk factors associated with this condition.
Additionally, it will discuss prevention and management strategies, emergency treatment options, and the long-term complications that may arise if left untreated.
By promoting hypertension awareness and education, individuals can be empowered to recognize the signs of a hypertensive crisis and take prompt action to seek necessary medical assistance.
Key Takeaways
- Recognize signs of hypertensive crisis
- Seek immediate medical attention
- Importance of regular blood pressure monitoring
- Help individuals recognize the importance of seeking immediate medical help
Understanding Hypertension and Hypertensive Crisis
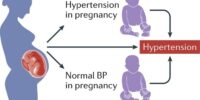
Hypertension, a condition characterized by elevated blood pressure, can potentially lead to a hypertensive crisis, which is an urgent medical situation requiring immediate attention.
A hypertensive crisis occurs when blood pressure reaches extremely high levels, typically above 180/120 mmHg.
There are two types of hypertensive crises: hypertensive urgency, which involves severely high blood pressure without acute organ damage, and hypertensive emergency, which involves both severely high blood pressure and acute organ damage.
The causes of a hypertensive crisis can vary and may include medication noncompliance, kidney disease, adrenal gland disorders, and drug interactions.
It is essential to seek immediate medical help when experiencing symptoms such as severe headache, shortness of breath, chest pain, blurred vision, and neurological deficits.
Management of a hypertensive crisis typically involves rapid blood pressure reduction through intravenous medications under close medical supervision. This process aims to prevent further organ damage and complications.
Prompt recognition of a hypertensive crisis and seeking immediate medical assistance is crucial to avoid potentially life-threatening complications.
Signs and Symptoms of a Hypertensive Crisis
Indications of a hypertensive crisis can include severe headaches, shortness of breath, chest pain, and vision changes. These symptoms may arise due to a sudden and severe increase in blood pressure, which can lead to organ damage and potentially life-threatening complications.
It is crucial to promptly recognize these signs and seek immediate medical help. However, it is important to note that diagnosing a hypertensive crisis requires a healthcare professional to measure blood pressure levels accurately.
Treatment for a hypertensive crisis typically involves lowering blood pressure levels to a safe range through the administration of intravenous medications. In addition, identifying and addressing any underlying causes that may have triggered the crisis is essential to prevent future episodes.
Consequently, timely recognition, diagnosis, and appropriate treatment are vital in managing hypertensive crises effectively.
Knowing When to Seek Immediate Medical Help
Prompt medical attention is crucial when experiencing severe symptoms such as intense headaches, difficulty breathing, chest discomfort, or changes in vision, as they may indicate a hypertensive crisis.
Recognizing these warning signs is essential in seeking emergency care promptly. Identifying a hypertensive crisis can be challenging, as symptoms may vary depending on the individual. However, common indicators include severe headache, shortness of breath, chest pain, blurred vision, confusion, and seizures.
If any of these symptoms occur, it is vital to seek immediate medical help. Ignoring these signs can lead to life-threatening complications such as stroke, heart attack, or organ damage.
Furthermore, it is crucial to inform healthcare professionals about any previous history of hypertension or medication non-compliance to ensure appropriate management of the hypertensive crisis.
Therefore, recognizing warning signs and seeking emergency care promptly can significantly improve outcomes for individuals experiencing a hypertensive crisis.
Risk Factors for Hypertensive Crisis
Identifying the risk factors associated with a hypertensive crisis is crucial for understanding the potential triggers and preventive measures. To further explore this topic, here are four important risk factors to consider:
- Age: Hypertensive crisis is more common in individuals above the age of 65. Aging leads to a natural increase in blood pressure, making older adults more susceptible.
- Obesity: Excess body weight puts additional strain on the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of hypertensive crisis. Maintaining a healthy weight through lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise and a balanced diet is essential.
- Medication Non-adherence: Failing to follow prescribed medication regimens can lead to uncontrolled blood pressure and potentially trigger a hypertensive crisis. Adhering to medication schedules is crucial for managing hypertension effectively.
- Co-existing Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or kidney disease, can exacerbate hypertension and increase the risk of a crisis. Managing these conditions and closely monitoring blood pressure is vital.
By understanding these risk factors and implementing necessary lifestyle modifications and medication adherence, individuals can reduce the likelihood of experiencing a hypertensive crisis.
Prevention and Management Strategies
Preventive measures and management strategies play a crucial role in mitigating the risk of hypertensive crisis and ensuring long-term cardiovascular health. Prevention strategies primarily focus on lifestyle modifications, aiming to control blood pressure levels and reduce the likelihood of a crisis. These strategies include maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, reducing salt and alcohol intake, and adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Additionally, it is important to manage stress levels through relaxation techniques and adequate sleep. Regular monitoring of blood pressure is essential to detect any changes and take appropriate action promptly. By adhering to these preventive measures and incorporating healthy habits into daily routines, individuals can effectively reduce their risk of hypertensive crisis and promote overall cardiovascular well-being.
| Prevention Strategies | Lifestyle Modifications |
|---|---|
| Maintain a healthy weight | Engage in regular physical activity |
| Reduce salt and alcohol intake | Adopt a balanced diet |
| Manage stress levels | Monitor blood pressure regularly |
| Get adequate sleep |
Emergency Treatment for Hypertensive Crisis
In emergency situations, medical professionals employ a range of interventions to swiftly address and stabilize individuals experiencing a hypertensive crisis. When faced with a hypertensive urgency, the following emergency treatments are typically utilized:
- Medications: Intravenous antihypertensive drugs like nitroprusside, labetalol, or nicardipine may be administered to rapidly reduce blood pressure levels.
- Continuous monitoring: Frequent monitoring of blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation helps in assessing the effectiveness of treatment and ensuring patient safety.
- Fluid management: Intravenous fluids may be administered cautiously to maintain adequate hydration and prevent complications.
- Close observation and supportive care: Patients are closely observed for any signs of organ damage, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or neurological symptoms, and appropriate interventions are initiated promptly.
These interventions aim to rapidly lower blood pressure while minimizing the risk of complications associated with hypertensive crises. Prompt medical attention is crucial in managing this emergency situation effectively.
Long-Term Complications of Untreated Hypertensive Crisis
Untreated hypertensive crisis can lead to severe long-term complications, including cardiovascular complications and organ damage. The sustained high blood pressure during a hypertensive crisis puts immense strain on the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of developing various cardiovascular conditions. These complications may include heart failure, coronary artery disease, stroke, and kidney damage.
The excessive pressure on the blood vessels can cause them to weaken and narrow, leading to atherosclerosis and subsequent cardiovascular events. Furthermore, the persistent elevated blood pressure can damage organs such as the heart, brain, kidneys, and eyes. Over time, this can result in significant dysfunction and irreversible damage to these vital organs.
It is crucial to recognize the signs of hypertensive crisis and seek immediate medical attention to prevent these potentially life-threatening complications.
Promoting Hypertension Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness and providing education about hypertension can play a crucial role in empowering individuals to take control of their cardiovascular health. Hypertension awareness campaigns and educating communities about hypertension are effective strategies to promote early recognition and management of hypertensive crisis.
- Hypertension awareness campaigns: These campaigns aim to disseminate information about the signs and symptoms of hypertensive crisis, as well as the importance of regular blood pressure monitoring. They can be conducted through various channels, such as social media, community events, and healthcare facilities.
- Educating communities about hypertension: Community education programs can provide valuable knowledge about the risk factors, complications, and preventive measures associated with hypertension. This can help individuals recognize the importance of seeking immediate medical help in case of a hypertensive crisis, thus reducing the likelihood of long-term complications.
By implementing these initiatives, individuals can be empowered to make informed decisions about their cardiovascular health, ultimately leading to better outcomes in the management of hypertensive crisis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the average age range for individuals who experience a hypertensive crisis?
The average age range for individuals experiencing a hypertensive crisis varies, but it is commonly observed in middle-aged and older adults. Risk factors associated with hypertensive crisis include a history of high blood pressure, medication non-adherence, and certain medical conditions.
Can a hypertensive crisis be triggered by certain foods or beverages?
Certain foods and beverages can potentially trigger a hypertensive crisis. These triggers may include high-sodium foods, excessive alcohol consumption, and stimulants like caffeine. It is important for individuals with hypertension to be mindful of their diet and avoid these potential triggers.
Are there any alternative therapies or natural remedies that can help manage a hypertensive crisis?
Alternative therapies and natural remedies are not recommended for managing a hypertensive crisis. Immediate medical intervention is crucial in such cases. It is important to recognize the symptoms and seek immediate medical help.
Can stress or anxiety contribute to the development of a hypertensive crisis?
Stress and anxiety can contribute to the development and worsening of hypertension, but their direct role in hypertensive crisis is not well established. Further research is needed to fully understand their impact on this condition.
Are there any specific medications that should be avoided if you are at risk for a hypertensive crisis?
In the management of hypertensive crisis, certain medications should be avoided. These include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), decongestants, and illicit drugs such as cocaine and amphetamines, as they can exacerbate hypertension and lead to a hypertensive crisis.