The Impact Of Stress On Blood Pressure: Managing The Connection
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While there are several factors that contribute to high blood pressure, stress is one of the leading causes.
Chronic stress has been shown to have a significant impact on blood pressure levels, which can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other health problems.
Understanding the link between stress and blood pressure is crucial for managing this condition effectively. By identifying stress triggers and implementing coping mechanisms, individuals can reduce their stress levels and improve their blood pressure readings.
This article will explore the effects of chronic stress on blood pressure, strategies for identifying stress triggers and coping mechanisms, and techniques for managing stress through exercise, mindfulness, and relaxation. By incorporating these practices into daily life, individuals can take control of their health and reduce the impact of stress on their blood pressure.
Key Takeaways
- Chronic stress significantly impacts blood pressure levels and increases the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Effective stress management techniques like relaxation techniques, exercise, and cognitive-behavioral therapy can help reduce the impact of stress on blood pressure.
- Practicing relaxation techniques can lower blood pressure, reduce muscle tension, and improve sleep quality, contributing to overall well-being.
- Seeking professional help can provide the necessary support and guidance to manage stress and hypertension effectively, including medication, therapy, and lifestyle recommendations.
Understanding the Link Between Stress and Blood Pressure
The relationship between stress and blood pressure has been extensively researched, revealing a strong association between the two physiological responses.
Stress is an inevitable part of life, but its long-term effects on health can be detrimental.
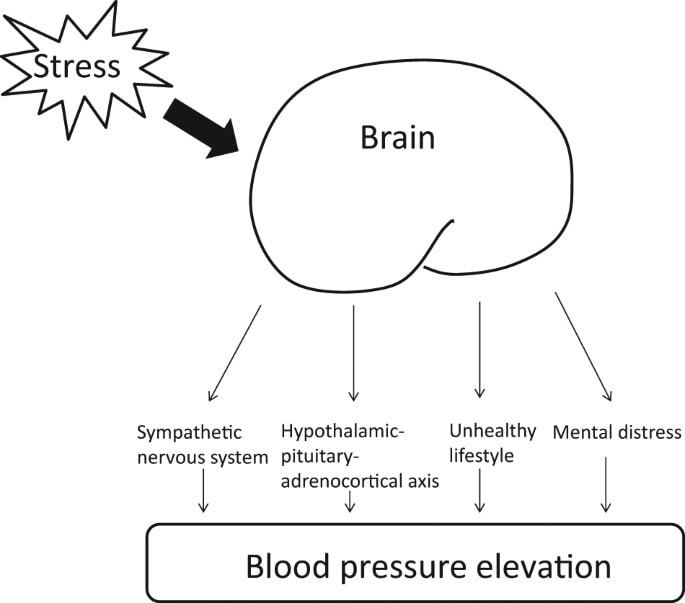
When the body experiences stress, the brain signals the release of hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol, which cause the heart to beat faster and increase blood pressure.
In the short term, this response is beneficial as it prepares the body for a fight-or-flight response; however, when the stressor persists, the constant increase in blood pressure can lead to hypertension, which is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke.
The link between stress and blood pressure has been studied for many years, and research has revealed that chronic stress can lead to long-term changes in blood pressure regulation.
In addition to the release of hormones, stress can also cause inflammation, which can damage blood vessels and contribute to hypertension.
Understanding the link between stress and blood pressure is crucial for managing blood pressure and preventing associated health complications.
While it is impossible to completely eliminate stress from our lives, there are effective stress management techniques such as exercise, meditation, and deep breathing that can help reduce the impact of stress on blood pressure.
The Effects of Chronic Stress on Blood Pressure
Chronic stressors have been shown to contribute to adverse cardiovascular outcomes, including hypertension and increased risk of heart disease. The physiological mechanisms underlying the link between chronic stress and high blood pressure are complex and multifactorial. Here are some key points to consider:
- Chronic stress leads to a sustained activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, resulting in the release of stress hormones such as cortisol and epinephrine. These hormones cause vasoconstriction and increase the heart rate, which can lead to a rise in blood pressure.
- Chronic stress also triggers the sympathetic nervous system (SNS), which releases noradrenaline and adrenaline. These hormones cause the heart to beat faster and stronger, increasing the force against the arterial walls and contributing to hypertension.
- Chronic stress can also cause inflammation, which is associated with the development of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease.
- The effects of chronic stress on blood pressure are cumulative and may become more pronounced over time.
- Effective stress management techniques, such as relaxation techniques, exercise, and cognitive-behavioral therapy, can help reduce the impact of chronic stress on blood pressure and cardiovascular health.
As such, it is crucial to recognize the role of chronic stress in hypertension and heart disease and take proactive steps to manage stress in order to maintain optimal blood pressure and overall cardiovascular health.
Identifying Stress Triggers and Coping Mechanisms
Identifying the triggers of stress and learning effective coping mechanisms are crucial steps in maintaining optimal cardiovascular health. Stress triggers vary from person to person and can be physical, environmental, or emotional.
Some common physical triggers of stress include lack of sleep, poor diet, and physical illness. Environmental triggers can include noise, pollution, and overcrowding. Emotional triggers may include work-related stress, relationship problems, or financial worries.
Identifying these triggers is the first step in managing stress and preventing its negative impact on blood pressure. Once stress triggers are identified, effective coping mechanisms can be employed to manage stress levels.
Coping mechanisms can be categorized into two types: problem-focused coping and emotion-focused coping. Problem-focused coping involves finding a solution to the source of stress, such as seeking help from a professional or making lifestyle changes. Emotion-focused coping involves managing the emotional response to stress, such as practicing relaxation techniques or seeking support from friends and family.
A combination of both problem-focused and emotion-focused coping mechanisms can be effective in managing stress and preventing its negative impact on blood pressure. It is important to find coping mechanisms that work for each individual, as what works for one person may not work for another.
Exercise and Physical Activity for Stress Relief
Exercise and physical activity have been shown to effectively reduce stress levels and improve cardiovascular health.
Aerobic exercise, such as running or cycling, increases blood flow and oxygen to the brain, which can improve mood and cognitive function.
Additionally, exercise stimulates the release of endorphins, which are natural mood-boosters and can help reduce feelings of anxiety and depression.
In terms of managing the connection between stress and blood pressure, regular physical activity can help lower blood pressure over time.
When we exercise, our heart works harder to pump blood, which strengthens the heart muscle and can help lower resting blood pressure.
Additionally, exercise can help reduce inflammation in the body, which is a contributing factor to high blood pressure.
Overall, incorporating exercise and physical activity into a daily routine can be a helpful tool in managing stress and improving cardiovascular health.
Mindfulness and Meditation Techniques
One effective strategy for reducing stress and promoting overall well-being is the practice of mindfulness and meditation techniques.
Mindfulness involves being present in the moment, focusing on the sensations in the body and the breath, and accepting thoughts and feelings without judgment.
Meditation involves similar techniques, but with a more structured approach.
Both mindfulness and meditation have been shown to have a positive impact on mental health, including reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression, and improving overall well-being.
To evoke emotion in the audience, here are five benefits of mindfulness and meditation techniques:
- Increased self-awareness and self-acceptance
- Improved ability to manage stress and regulate emotions
- Greater feelings of calm and relaxation
- Increased compassion and empathy for oneself and others
- Improved ability to focus and concentrate
Improving Sleep Quality to Reduce Stress
Transition: While mindfulness and meditation techniques can be effective in managing stress levels, another important aspect of stress management is improving sleep quality. In fact, poor sleep quality is often linked to higher levels of stress and can have a negative impact on blood pressure.
The connection between sleep and stress is complex and bidirectional. On one hand, stress can lead to poor sleep quality by causing hyperarousal and disrupting the natural sleep-wake cycle. On the other hand, lack of sleep can also increase stress levels by affecting mood, cognitive function, and overall well-being. In addition, research has shown that individuals with poor sleep quality are more likely to develop hypertension, a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
Therefore, improving sleep quality is crucial for reducing stress and maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
To improve sleep quality, there are several strategies that can be implemented. One of the most effective ways is to establish a consistent sleep routine by going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate the circadian rhythm and promote better sleep. Other strategies include creating a relaxing sleep environment, avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bedtime, and engaging in regular physical activity.
By incorporating these strategies into daily life, individuals can improve their sleep quality and reduce the negative impact of stress on blood pressure.
Incorporating Relaxation Techniques into Daily Life
Incorporating relaxation techniques into daily life can offer a practical approach to reducing the negative effects of stress on overall well-being. Relaxation techniques are designed to help individuals achieve a state of calmness and relaxation, which can help to reduce stress levels. These techniques can be practiced in a variety of settings, including at home, at work, or even while commuting.
Some examples of relaxation techniques that can be incorporated into daily life include:
- Deep breathing exercises
- Yoga
- Meditation
By incorporating these techniques into daily life, individuals can help to reduce the negative effects of stress on their overall health and well-being. Research has shown that practicing relaxation techniques can help to lower blood pressure, reduce muscle tension, and improve sleep quality. Additionally, these techniques can help to reduce anxiety and improve mood, which can further contribute to overall well-being.
It is important to note that incorporating relaxation techniques into daily life is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Different individuals may find different techniques more effective, and it may take some trial and error to find the right approach. However, with practice and persistence, individuals can learn to incorporate relaxation techniques into their daily routine, and reap the benefits of reduced stress levels and improved overall health.
Seeking Professional Help for Chronic Stress and High Blood Pressure Management
Professional help from healthcare providers can be an effective approach for managing chronic stress and hypertension. Chronic stress can have a significant impact on blood pressure, and if left unmanaged, it can lead to hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases. Seeking professional help can help individuals identify the underlying causes of their stress and develop effective coping strategies to manage it.
There are various healthcare professionals who can help individuals manage stress and hypertension. These may include primary care physicians, psychologists, psychiatrists, and other mental health professionals. These professionals can provide medication, therapy, or a combination of both to help individuals manage their stress and blood pressure. Additionally, they can offer lifestyle recommendations such as exercise, healthy eating habits, and stress-reducing activities.
Seeking professional help can provide individuals with the necessary support and guidance to manage their stress and hypertension effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, stress and blood pressure are closely linked, and chronic stress can significantly increase the risk of hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases.
Identifying stress triggers and implementing effective coping mechanisms, such as exercise, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques, can help manage stress and keep blood pressure under control.
Adequate sleep and seeking professional help are also crucial in managing chronic stress and hypertension.
In addition to managing stress, making healthy lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a balanced diet, limiting alcohol and tobacco use, and getting regular physical activity can also help prevent and manage high blood pressure.
By taking proactive steps to manage stress and adopting healthy habits, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of hypertension and improve their overall health and well-being.