What Are Antianxiety Medications And How Do They Treat Panic Disorders?
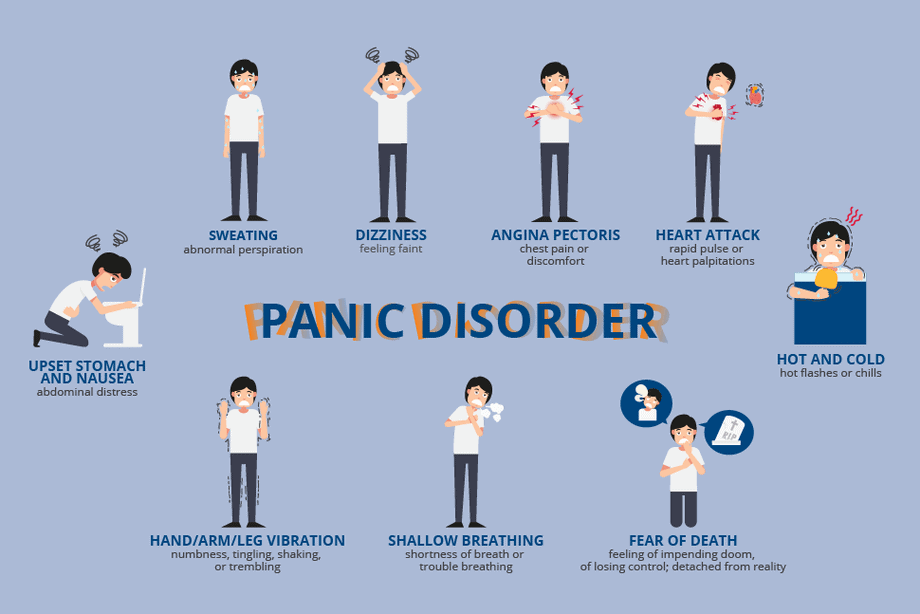
Panic disorders are characterized by recurrent and unexpected episodes of intense fear or discomfort, often accompanied by physical symptoms such as heart palpitations, shortness of breath, and dizziness. These episodes can significantly impair an individual’s daily functioning and quality of life.
Antianxiety medications are commonly used to treat panic disorders and alleviate the symptoms associated with them. This article aims to provide an overview of antianxiety medications and their role in the treatment of panic disorders. It will discuss the different classes of antianxiety medications, including benzodiazepines, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), and beta blockers. Additionally, other medications used for panic disorders will be explored.
It is important to note that seeking professional help is crucial when considering the use of antianxiety medications for panic disorders, as a comprehensive evaluation and individualized treatment plan are necessary for optimal outcomes.
Key Takeaways
- Antianxiety medications, such as beta blockers and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), are commonly prescribed for panic disorders.
- These medications can help reduce the physical symptoms of panic attacks, such as heart rate and blood pressure.
- However, they are not standalone treatments and are usually used in combination with other interventions, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT).
- While antianxiety medications can provide short-term relief, they may have side effects like fatigue and dizziness, and long-term use may lead to more serious side effects. Regular monitoring and communication with healthcare professionals are important.
Understanding Panic Disorders
Panic disorders are characterized by sudden and repeated episodes of intense fear and discomfort, often accompanied by physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, and dizziness. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and triggers of panic disorders is essential for effective management and treatment.
Symptoms can vary from person to person, but common ones include chest pain, trembling, sweating, and a sense of impending doom. Panic attacks can be triggered by certain situations or events, such as crowded spaces or public speaking.
It is important for individuals with panic disorders to develop effective coping strategies for managing panic attacks. These strategies may include deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and cognitive-behavioral therapy.
Additionally, medication can be prescribed to help alleviate symptoms and reduce the frequency and severity of panic attacks. Antianxiety medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and benzodiazepines, are commonly used in the treatment of panic disorders.
What are Antianxiety Medications?
Anxiety disorders can be effectively managed with the use of pharmaceutical interventions specifically designed to alleviate symptoms and promote a sense of calm and relaxation.
One type of medication commonly prescribed for anxiety disorders is antianxiety medications. These medications, such as benzodiazepines and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), work by targeting the brain’s neurotransmitters to reduce anxiety and induce a calming effect.
Benzodiazepines, such as Xanax and Valium, act as central nervous system depressants, enhancing the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that inhibits brain activity. This results in a sedative effect and reduced anxiety levels.
On the other hand, SSRIs, like Prozac and Zoloft, work by increasing the availability of serotonin, a neurotransmitter associated with mood regulation, thereby reducing anxiety symptoms.
It is important to note that these medications may have side effects, including drowsiness, dizziness, and potential dependency, so careful monitoring and supervision by a healthcare professional is necessary when using antianxiety medications.
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines, a class of pharmaceutical interventions, act as central nervous system depressants, targeting the brain’s neurotransmitters to induce a sedative effect and reduce levels of anxiety. These medications enhance the inhibitory effects of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), resulting in a calming and relaxing effect on the body. Commonly prescribed benzodiazepines include diazepam, alprazolam, and lorazepam.
While benzodiazepines are effective in the short-term treatment of panic disorders and other anxiety-related conditions, they are associated with potential risks and drawbacks. Benzodiazepine addiction is a concern, as these medications can lead to dependence and withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation. Prolonged use of benzodiazepines can also have long-term effects, such as cognitive impairment, memory problems, and increased risk of falls in older adults. Therefore, careful monitoring and individualized treatment plans are necessary to ensure the safe and appropriate use of benzodiazepines in managing panic disorders.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Rapid onset of action | Risk of addiction |
| Effective in acute episodes | Sedation and drowsiness |
| Wide range of options | Cognitive impairment |
| Management of symptoms | Memory problems |
| Short-term relief | Increased risk of falls in older adults |
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) are a commonly prescribed class of pharmaceutical interventions that target the brain’s neurotransmitters to alleviate symptoms related to anxiety disorders. When it comes to panic disorder, SSRIs have shown efficacy in reducing the frequency and severity of panic attacks.
Here are some key points about SSRIs and their role in treating panic disorder:
- SSRIs work by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain, which helps regulate mood and emotions.
- They are considered a first-line treatment for panic disorder due to their effectiveness and relatively low risk of addiction.
- Common SSRI medications used for panic disorder include sertraline, fluoxetine, and escitalopram.
- Side effects of SSRIs may include nausea, insomnia, sexual dysfunction, and weight gain.
- Management of SSRI side effects can involve adjusting the dosage, switching to a different medication, or adding adjunct medications.
It is important to note that the use of SSRIs for panic disorder should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as individual responses to medication can vary.
Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are another class of pharmaceutical interventions commonly prescribed for the treatment of panic disorder, targeting neurotransmitters in the brain to alleviate symptoms.
SNRIs, such as venlafaxine and duloxetine, work by inhibiting the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine in the synaptic cleft, leading to increased levels of these neurotransmitters. This increased availability of serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain helps regulate mood and reduce anxiety symptoms associated with panic disorder.
SNRIs are considered an alternative treatment option for individuals who do not respond well to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or who experience intolerable side effects. However, it is important to note that the effectiveness of SNRIs may vary among individuals, and the decision to prescribe SNRIs should be made on a case-by-case basis, considering the patient’s specific needs and medical history.
Beta Blockers
This paragraph will discuss the key points of how beta blockers work, their use in panic disorder treatment, and potential side effects.
Beta blockers are a class of medications that primarily work by blocking the effects of adrenaline on beta receptors in the body.
In the context of panic disorder treatment, beta blockers are sometimes prescribed to help manage the physical symptoms of anxiety, such as rapid heart rate and palpitations.
However, it is important to note that beta blockers may have potential side effects, including fatigue, dizziness, and sexual dysfunction.
How Beta Blockers Work
Beta blockers are commonly used to treat panic disorders by blocking the effects of adrenaline, which decreases heart rate and blood pressure, helping to reduce the physical symptoms of anxiety.
These medications work by binding to beta-adrenergic receptors, preventing the activation of these receptors by adrenaline. This mechanism of action reduces the body’s response to stress and anxiety-inducing situations.
By blocking the effects of adrenaline, beta blockers can effectively reduce heart palpitations, tremors, and sweating, which are common symptoms experienced during panic attacks.
However, it is important to note that beta blockers primarily target the physical symptoms of anxiety and may not directly address the underlying psychological aspects of panic disorders. Therefore, they are often used in conjunction with other medications or therapies to provide comprehensive treatment for individuals suffering from panic disorders.
Use in Panic Disorder Treatment
Panic disorder treatment often involves the use of beta blockers in conjunction with other therapies to address both the physical and psychological symptoms of the disorder. Beta blockers, such as propranolol, work by blocking the effects of adrenaline, which can reduce heart rate and blood pressure, helping to alleviate some of the physical symptoms associated with panic attacks. However, it is important to note that beta blockers are not a standalone treatment for panic disorder and are typically used as an adjunct to other interventions.
In addition to beta blockers, the use of cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a common treatment approach for panic disorder. CBT aims to identify and modify negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to panic attacks. This therapy can help individuals develop coping mechanisms and strategies to manage anxiety and prevent future panic attacks.
While beta blockers and CBT are often effective in managing panic disorder, there are also alternative treatments that individuals may consider. These may include relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises and mindfulness meditation, as well as lifestyle modifications like regular exercise and adequate sleep. It is important for individuals to work with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for their specific needs.
| Pros of Beta Blockers in Panic Disorder Treatment | Cons of Beta Blockers in Panic Disorder Treatment |
|---|---|
| Effective in reducing physical symptoms of panic attacks | Can cause side effects such as fatigue and dizziness |
| Can be used as a short-term solution for immediate relief | May not address the underlying causes of panic disorder |
| Can be used in combination with other therapies | Requires careful monitoring of blood pressure and heart rate |
| Can help individuals manage anxiety in high-stress situations | May not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions |
Potential Side Effects
The potential side effects of using beta blockers in the treatment of panic disorder can have a significant impact on an individual’s overall well-being. While beta blockers are generally well-tolerated, there are some common side effects that individuals may experience. These include fatigue, dizziness, and low blood pressure. Although these side effects are usually mild and temporary, they can still interfere with daily activities and quality of life.
Additionally, long-term use of beta blockers may result in more serious side effects such as depression, sexual dysfunction, and weight gain. It is important for individuals taking beta blockers to be aware of these potential side effects and to discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider. Regular monitoring and communication with healthcare professionals can help to manage and minimize these side effects, ensuring the best possible outcome for individuals with panic disorder.
Other Medications for Panic Disorders
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly prescribed medications for panic disorders. While antianxiety medications are effective in treating panic disorders, there are other options available for individuals who may not respond well to or prefer not to take medication.
Alternative treatments such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), relaxation techniques, and mindfulness meditation have shown promise in managing panic symptoms. CBT focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to panic attacks. Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises and progressive muscle relaxation, aim to reduce physical tension and promote a sense of calm.
Additionally, lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, adequate sleep, and a healthy diet can play a significant role in managing panic disorder symptoms. It is important for individuals to discuss these alternatives with their healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment approach for their specific needs.
Seeking Professional Help
Seeking professional help from a trained healthcare provider is crucial in effectively managing and finding appropriate treatment for individuals experiencing symptoms of panic disorders. Professional therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), is often recommended as a first-line treatment for panic disorders. CBT focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to panic attacks. It helps individuals develop coping strategies and techniques to manage and reduce anxiety symptoms.
In addition to therapy, healthcare providers may also recommend alternative treatments such as relaxation techniques, mindfulness meditation, and exercise. These can help individuals with panic disorders learn to manage stress, reduce anxiety, and promote overall well-being.
However, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable treatment approach based on individual needs and circumstances.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are there any natural alternatives to antianxiety medications for treating panic disorders?
Natural remedies, lifestyle changes, herbal supplements, and therapy options can serve as alternatives to antianxiety medications for treating panic disorders. These methods offer potential benefits in managing symptoms and promoting overall well-being.
Can antianxiety medications be used to treat other mental health conditions, such as depression or obsessive-compulsive disorder?
Antianxiety medications can be used to treat other mental health conditions such as depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder. They may also be prescribed for bipolar disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder.
How long does it typically take for antianxiety medications to start working and alleviate panic disorder symptoms?
The effectiveness of antianxiety medications in treating panic disorder symptoms varies among individuals. Generally, it takes several weeks for these medications to start working and alleviate panic disorder symptoms.
Are antianxiety medications addictive?
Antianxiety medications can be addictive, although the risk varies depending on the specific medication and individual factors. It is important to consider alternative treatments and be aware of potential long-term effects of antianxiety medications.
What are the potential side effects of taking antianxiety medications for panic disorders?
Potential side effects of antianxiety medications used for panic disorders include drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, and memory problems. Long-term effects may include dependency, withdrawal symptoms, and cognitive impairment, although individual experiences vary.