What are the 4 worst blood pressure drugs
4 worst blood pressure drugs
Clinical research highlights that methyldopa (Aldomet), clonidine (Catapres), thiazide diuretics, and reserpine have well-documented side effects, which may outweigh their benefits for some patients.
Methyldopa can cause drowsiness and depression; clonidine carries risks of hypotension and dizziness; thiazide diuretics may lead to electrolyte imbalances, and reserpine has been linked to depression and psychiatric effects.
Why these medications are considered some of the worst choices for blood pressure management? Facts are supported by decades of clinical research and patient safety data.
Studies that support the data
- Methyldopa (Aldomet): Studies dating back to the 1950s highlight concerns over drowsiness, depression, and dry mouth. These side effects, documented in clinical research, affect tolerability, especially in long-term usage. Studies on methyldopa (Aldomet) were conducted by researchers like Dollery and Harrington in the early 1960s.
- Clonidine (Catapres): Clonidine has been studied since the 1960s, revealing risks of hypotension, dizziness, and sedation. The drug’s effects on blood pressure and the need for controlled dosing are supported by clinical trials showing precise dosing requirements to minimize these risks. Researchers like Robinson, Keshavan, and McEntee contributed significantly to understanding clonidine’s side effects and its complex dosing requirements.
- Thiazide Diuretics: Studies from the 1950s onward document electrolyte imbalances, particularly hypokalemia (low potassium), affecting heart rhythm. Consistent monitoring practices recommended in prescribing guidelines stem from evidence of these electrolyte side effects. Early studies were conducted by Dr. Edward Freis and colleagues, who linked thiazide-induced potassium depletion to risks in patients with cardiovascular issues. Further research by Dr. George E. Schreiner and Dr. John H. Laragh expanded on electrolyte imbalances
- Reserpine: Clinical studies from the mid-20th century found depression, sedation, and psychiatric effects associated with reserpine, leading to its classification as a non-preferred treatment. These side effects, thoroughly documented in clinical literature, explain why it is generally avoided as a first-line hypertension medication. Pioneers in these studies included Dr. Edward Freis, who examined reserpine’s potential in hypertension and noted its significant sedative and depressogenic effects, and researchers like Dr. Frederick Goodwin and Dr. John Bunney
Modern research on 4 worst blood pressure drugs
Modern research on methyldopa, clonidine, thiazide diuretics, and reserpine emphasizes the need for targeted use due to their side effects and the availability of newer antihypertensive agents.
Methyldopa
Methyldopa is still prescribed in specific cases, such as for pregnant women with hypertension due to its relatively safer profile during pregnancy. However, its sedative effects, potential for depression, and risk of liver toxicity limit its general use compared to newer drugs with fewer central nervous system effects.
Clonidine
Clonidine remains a secondary or adjunct treatment for hypertension and is also used off-label for conditions like ADHD and withdrawal symptoms due to its calming effects on the central nervous system. Modern studies confirm that while clonidine is effective, it is often avoided as a primary treatment for hypertension due to risks of severe sedation, hypotension, and rebound hypertension if stopped suddenly. This limits its use to cases where other antihypertensives are unsuitable.
Thiazide Diuretics
Thiazide diuretics, including hydrochlorothiazide and chlorthalidone, are still commonly recommended as first-line treatments for hypertension because they reduce cardiovascular events. However, studies emphasize the need for careful monitoring of electrolyte levels, particularly potassium, due to the risk of hypokalemia. Some modern guidelines suggest combining thiazides with potassium-sparing agents to mitigate these side effects and improve safety profiles.
Reserpine
Reserpine is rarely used in modern hypertension treatment due to its significant side effects, particularly the risk of depression and sedation. Although it was once a staple in hypertension therapy, its role has diminished with the advent of medications that effectively lower blood pressure without impacting mental health as severely. Research now focuses on alternatives that do not deplete neurotransmitters, reducing the likelihood of depression and other psychiatric effects.
Common Side Effects
| Drug | Common Side Effects | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Methyldopa (Aldomet) |
|
Various studies, Drugs.com, MedlinePlus |
| Clonidine (Catapres) |
|
NIH, Cochrane Review, Drugs.com |
| Thiazide Diuretics |
|
Cochrane Review, Mayo Clinic, Healthline |
| Reserpine |
|
Journal of Psychopharmacology, Drugs.com, American Family Physician |
The perception of these medications as “worst” may be influenced by factors such as side effect profiles, newer treatment options with fewer side effects, and individual patient needs and preferences. However, it’s essential to emphasize that no medication is universally “worst” or “best” for all patients, and the choice of medication should be made on a case-by-case basis, considering the patient’s overall health, medical history, and individual responses to treatment.
Effectiveness of blood pressure medications and side effects can vary from person to person. Let’s take a closer look at these 4 worst blood pressure drugs individually.
Aldomet side effects
Aldomet (methyldopa) is a medication that was commonly used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) in the past, but its use has declined in recent years due to the availability of more effective and safer alternatives.
Aldomet has been associated with a high risk of severe side effects, including blood disorders such as agranulocytosis (a condition where there is a severe decrease in white blood cells) and neurological problems such as depression, anxiety, confusion and hallucinations. These side effects are considered serious and can be life-threatening.
In addition, Aldomet can also cause liver damage and it should not be used by patients with liver disease.
Due to these potential side effects, the use of Aldomet has been significantly reduced and it is not recommended as first-line therapy for hypertension by most professional organizations and guidelines.
It’s important to note that Aldomet is not banned but its use is not recommended as first-line therapy for hypertension and it’s use is limited to certain specific cases under the guidance of a healthcare provider. And always report any side effects or adverse reactions to your healthcare provider, they will adjust the treatment accordingly.
Catapres side effects
Catapres (clonidine) is a medication that is used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) and certain other conditions. It is an alpha-2 adrenergic agonist, which means it works by reducing the activity of certain nerves in the body.
Catapres has been known to cause severe drowsiness and sedation, which can affect a person’s ability to perform daily activities. These side effects can be particularly dangerous when operating heavy machinery or driving a vehicle. It can also cause other side effects such as dry mouth, constipation, and fatigue.
In addition, Catapres has been associated with severe withdrawal symptoms if the medication is discontinued abruptly.
Due to these potential side effects and safety concerns, the use of Catapres has been significantly reduced and it is not recommended as first-line therapy for hypertension by most professional organizations and guidelines.
Catapres is not banned but its use is limited to certain specific cases under the guidance of a healthcare provider and it should not be discontinued abruptly without consulting with a healthcare provider first. And always report any side effects or adverse reactions to your healthcare provider, they will adjust the treatment accordingly.
Thiazide diuretics side effects
Thiazide diuretics are a class of medications that are used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension). They work by increasing the amount of salt and water that the kidneys remove from the blood, which in turn reduces the volume of fluid in the blood vessels and lowers blood pressure.
Thiazide diuretics can cause electrolyte imbalances, leading to problems such as low potassium levels (hypokalemia), which can cause muscle weakness, cramps, and irregular heartbeats. They can also lead to an increase in blood sugar and cholesterol levels. These side effects are considered serious and can be life-threatening.
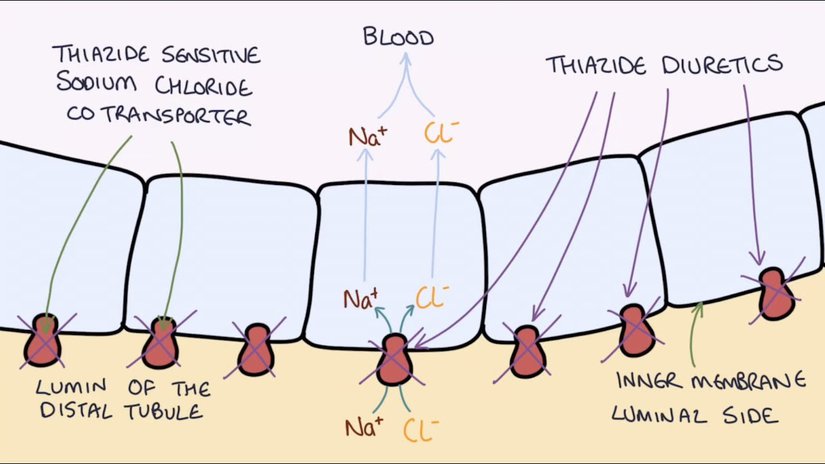
Thiazide diuretics are not banned and are still used as first-line therapy for hypertension by most professional organizations and guidelines. However, their use is limited to certain specific cases under the guidance of a healthcare provider and they should be used with caution, especially in patients with diabetes or heart disease. They are also recommended to be taken with potassium-sparing diuretics or potassium supplement to prevent the development of hypokalemia.
Thiazide diuretics can have different side effects on different individuals and always report any side effects or adverse reactions to your healthcare provider, they will adjust the treatment accordingly.
Reserpine side effects
Reserpine is a medication that was used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure) and certain other conditions in the past, but its use has declined in recent years due to the availability of more effective and safer alternatives.
Reserpine can cause serious side effects such as depression, which can be severe and long-lasting. It can also cause drowsiness and sedation, which can affect a person’s ability to perform daily activities. Other side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and muscle weakness.
Due to these potential side effects, the use of Reserpine has been significantly reduced and it is not recommended as first-line therapy for hypertension by most professional organizations and guidelines.
Reserpine is not banned but its use is limited and it should not be used in patients with a history of depression or mental health issues. And always report any side effects or adverse reactions to your healthcare provider, they will adjust the treatment accordingly.
These 4 medications may be more appropriate for certain individuals, depending on their health condition, and they may be the best option for some patients. However, they should be used with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare provider. And always report any side effects or adverse reactions to your healthcare provider, they will adjust the treatment accordingly.
What is considered a “good” blood pressure drug
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to what is considered a “good” blood pressure medication because the choice of medication depends on an individual’s specific health conditions, medical history, and how well they respond to the medication. However, there are several classes of blood pressure medications that are commonly used and considered effective in managing hypertension (high blood pressure). These medications include:
- Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors: Examples include lisinopril, enalapril, and ramipril. ACE inhibitors relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure by blocking the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a substance that narrows blood vessels.
- Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs): Examples include losartan, valsartan, and irbesartan. ARBs work by blocking the effects of angiotensin II, leading to blood vessel relaxation and lower blood pressure.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: These include amlodipine, diltiazem, and verapamil. They reduce blood pressure by relaxing blood vessel muscles and slowing the heart rate.
- Beta-Blockers: Examples include metoprolol, atenolol, and carvedilol. Beta-blockers decrease the heart rate and reduce the force of the heart’s contractions, leading to lower blood pressure.
- Diuretics: Thiazide diuretics, such as hydrochlorothiazide, are commonly prescribed. They help the body eliminate excess sodium and fluid, reducing the volume of blood and lowering blood pressure.
- Alpha-Blockers: Medications like doxazosin and prazosin relax certain muscles in the blood vessel walls, leading to decreased resistance and lower blood pressure.
- Alpha-2 Receptor Agonists: Clonidine is an example of this class. It works in the brain to decrease nerve signals that constrict blood vessels, resulting in lowered blood pressure.
- Direct Vasodilators: Hydralazine is an example of a direct vasodilator. It relaxes the muscles in the blood vessel walls, allowing blood vessels to widen and blood pressure to decrease.
- Combination Medications: In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe combination medications that contain two or more different types of antihypertensive drugs to address high blood pressure from different angles.
What is considered “good” in terms of blood pressure management varies depending on individual health goals and circumstances. A healthcare provider will determine the most appropriate medication or combination of medications based on factors such as the patient’s blood pressure readings, overall health, and any underlying medical conditions.
Remember that medication is often just one component of blood pressure management. Lifestyle modifications, including a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and reduced salt intake, are also crucial in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels. Ultimately, the best blood pressure medication for an individual should be determined through consultation with a healthcare provider.
Natural food instead of blood pressure medications?
Certain natural foods and dietary choices can contribute to lower blood pressure and support overall heart health. While they are not a replacement for prescribed medications in cases of high blood pressure, incorporating these foods into your diet can complement your hypertension management. Here are some natural foods that are considered beneficial for blood pressure:
- Leafy Greens: Vegetables like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are rich in potassium, which helps your body balance sodium levels and regulate blood pressure.
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries contain flavonoids called anthocyanins, which have been linked to blood pressure reduction.
- Beets: Beets are high in nitrates, which can help relax blood vessels and improve blood flow, potentially reducing blood pressure.
- Oats: Oats are a good source of soluble fiber, which can help lower blood pressure by reducing the amount of LDL (bad) cholesterol in your bloodstream.
- Bananas: Bananas are another potassium-rich food that can help offset the effects of sodium on blood pressure.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and trout are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which can lower blood pressure and reduce inflammation.
- Garlic: Garlic contains allicin, a compound that may help relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, flaxseeds, and chia seeds are rich in potassium, magnesium, and healthy fats that can benefit heart health and blood pressure.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and peas are excellent sources of fiber, potassium, and magnesium, all of which can support lower blood pressure.
- Low-Fat Dairy: Low-fat yogurt, milk, and cheese provide calcium and protein, which can be part of a balanced diet for blood pressure management.
- Dark Chocolate: Dark chocolate with at least 70% cocoa contains flavonoids that may help lower blood pressure when consumed in moderation.
- Pomegranates: Pomegranate juice is rich in antioxidants and may improve blood pressure by promoting nitric oxide production, which relaxes blood vessels.
- Hibiscus Tea: Some studies suggest that hibiscus tea may have a modest effect on lowering blood pressure due to its natural diuretic properties.
It’s important to note that while these foods can have a positive impact on blood pressure, they should be part of an overall heart-healthy diet. Reducing sodium intake, limiting processed and high-sodium foods, maintaining a healthy weight, and regular physical activity are also essential components of blood pressure management.
If you have hypertension or other cardiovascular concerns, consult with a healthcare professional for personalized dietary recommendations and a comprehensive treatment plan.
What’s next
- Consult Your Healthcare Provider:
Always consult with your healthcare provider or a qualified medical professional before making any decisions regarding your medications. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific health condition, medical history, and individual needs. - Ask About Alternative Medications:
If you have concerns about the side effects or suitability of a medication you’re currently taking, discuss these concerns with your healthcare provider. They can explore alternative medications or treatment options that may be better suited to your situation. - Medication Adherence:
If you’re prescribed any of these medications, it’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions carefully. Consistent medication adherence and regular follow-up appointments are crucial for managing hypertension effectively. - Educate Yourself:
Knowledge is empowering. Educate yourself about your condition and the medications you’re taking. Understand the potential side effects and what to watch for. This knowledge can help you make informed decisions and communicate effectively with your healthcare team. - Lifestyle Modifications:
In addition to medications, lifestyle changes such as a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and reducing salt intake can significantly impact blood pressure management. Discuss these lifestyle modifications with your healthcare provider. - Regular Monitoring:
If you’re on a medication that requires monitoring of specific parameters, like potassium levels with thiazide diuretics, make sure you attend regular check-ups and follow the recommended tests. - Patient Preferences:
It’s important to consider patient preferences and comfort when selecting a medication. Share your concerns and preferences with your healthcare provider so that they can work with you to find a treatment plan that you’re comfortable with. - Stay Informed:
Keep up with the latest research and medical guidelines. Healthcare is an evolving field, and new treatments and approaches may become available.
Remember that your healthcare provider is your primary source of guidance in managing your health. They can help you navigate the complexities of medication choices, potential side effects, and the best course of action for your specific medical situation. Always prioritize open and honest communication with your healthcare team for the best possible care and outcomes.