What Is Gestational Hypertension And How Is It Managed?
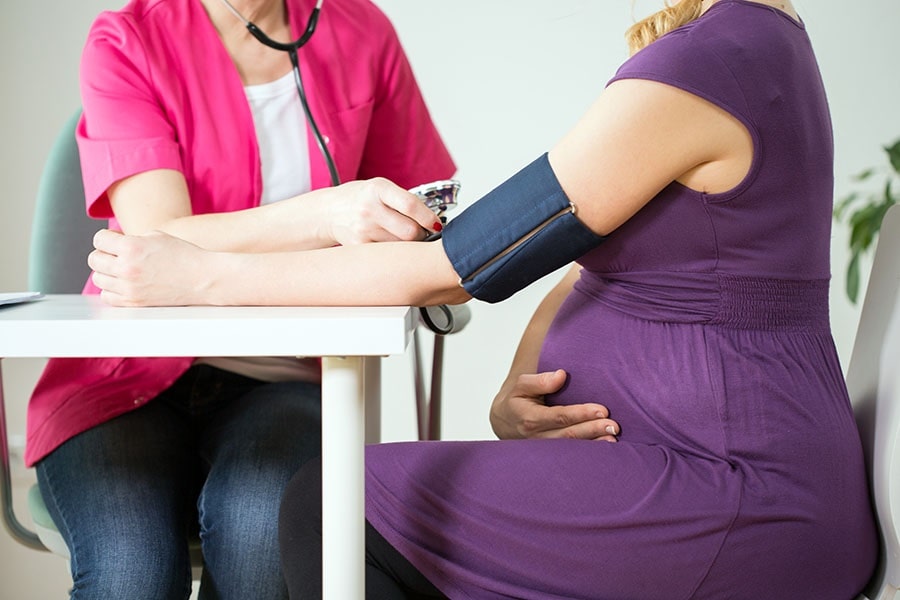

Gestational hypertension is a medical condition characterized by high blood pressure that occurs during pregnancy. It is a significant concern as it can lead to adverse maternal and fetal outcomes if not managed appropriately.
This article aims to provide an overview of gestational hypertension, including its definition, symptoms, causes, risk factors, potential complications, diagnosis, and monitoring. Additionally, it will discuss various management strategies, such as lifestyle changes, self-care measures, medications, and medical interventions.
The importance of regular prenatal care and monitoring for early detection and timely treatment will also be emphasized. By adhering to an academic style of writing, this article will present objective and impersonal information, focusing on the scientific understanding and management of gestational hypertension.
Key Takeaways
- Gestational hypertension is a condition characterized by high blood pressure during pregnancy.
- It is important to receive prenatal care and monitoring to detect and identify gestational hypertension early.
- Prompt interventions and treatment are necessary to manage gestational hypertension effectively.
- Lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes, regular exercise, and stress reduction techniques, can help in managing and preventing gestational hypertension.
Definition and Symptoms of Gestational Hypertension
Gestational hypertension, also known as pregnancy-induced hypertension, is characterized by high blood pressure that develops after the 20th week of pregnancy and resolves within 12 weeks after delivery. It is a common pregnancy complication, affecting around 6-8% of pregnancies.
The exact cause of gestational hypertension is unknown, but it is believed to be related to the placenta’s function. The condition is typically asymptomatic, and the only way to diagnose it is through regular blood pressure monitoring during prenatal visits. However, in some cases, women may experience symptoms such as severe headaches, blurred vision, abdominal pain, and swelling of the hands or face.
Prompt diagnosis and management of gestational hypertension are crucial to prevent complications such as preeclampsia and eclampsia, which can endanger both the mother and the baby. Treatment usually involves close monitoring of blood pressure, lifestyle modifications, and, in severe cases, medication.
Causes and Risk Factors of Gestational Hypertension
Causes and risk factors of gestational hypertension include family history of hypertension, obesity, older maternal age, multiple pregnancies, and underlying medical conditions such as diabetes or kidney disease. These factors contribute to the development of high blood pressure during pregnancy.
It is important to note that the exact cause of gestational hypertension is not fully understood. However, it is believed that the placenta plays a significant role in the development of this condition. The placenta releases certain substances that can affect blood vessel function and lead to high blood pressure.
Gestational hypertension can have serious implications for both the mother and the fetus. It increases the risk of complications such as preeclampsia and preterm birth.
To prevent or manage gestational hypertension, healthcare providers may recommend lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate rest. Additionally, close monitoring of blood pressure and fetal development is essential to ensure the well-being of both mother and baby.
Potential Complications of Gestational Hypertension
Potential complications of gestational hypertension include adverse effects on maternal cardiovascular health, such as an increased risk of cardiovascular disease in later life, as well as negative impacts on fetal growth and development, including the potential for intrauterine growth restriction and placental abruption.
Prevention strategies play a crucial role in managing gestational hypertension and minimizing its potential complications. Regular prenatal care, including blood pressure monitoring and early detection of hypertension, is essential. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight, adopting a balanced diet, and engaging in regular physical activity, can also help prevent or manage gestational hypertension. Additionally, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption is important.
The long-term effects of gestational hypertension are not limited to the pregnancy period. Women with a history of gestational hypertension are at an increased risk of developing chronic hypertension, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease later in life. Therefore, effective management and follow-up care are necessary to ensure the overall well-being of both the mother and the baby.
Diagnosis and Monitoring of Gestational Hypertension
Diagnosis and monitoring of gestational hypertension involves regular prenatal care and the implementation of strategies to detect and manage high blood pressure during pregnancy.
Early diagnosis is crucial for timely intervention and prevention of potential complications. To diagnose gestational hypertension, healthcare providers often rely on blood pressure measurements obtained during routine prenatal visits. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends that blood pressure be measured at every prenatal visit to monitor for any changes or abnormalities.
Additionally, other diagnostic methods such as urine tests, blood tests, and ultrasounds may be used to assess organ function and rule out other underlying conditions. Continuous blood pressure monitoring may be necessary in severe cases or when there are concerns about the well-being of the mother or baby.
Through regular monitoring and timely intervention, healthcare professionals can effectively manage gestational hypertension and ensure the best possible outcome for both mother and baby.
Lifestyle Changes and Self-Care Measures
Lifestyle changes and self-care measures play a crucial role in the management and prevention of complications associated with high blood pressure during pregnancy. These measures include dietary modifications and maintaining an appropriate exercise routine.
- Dietary modifications: A well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products can help to lower blood pressure. Limiting sodium intake and avoiding processed foods that are high in salt can also be beneficial.
- Exercise routine: Regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, can help to reduce blood pressure levels and improve overall cardiovascular health. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any exercise regimen during pregnancy to ensure its safety and suitability.
By implementing these lifestyle changes, women with gestational hypertension can actively participate in managing their condition and reduce the risk of complications for both themselves and their baby.
Medications and Medical Interventions
Medical interventions and medications are often necessary in the management of high blood pressure during pregnancy to ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby.
There are several medication options available for the treatment of gestational hypertension. Antihypertensive medications such as methyldopa, labetalol, and nifedipine are commonly prescribed to lower blood pressure. These medications are considered safe for use during pregnancy and have been shown to effectively control blood pressure without harming the fetus.
In addition to medication, non-pharmacological interventions, such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and stress reduction techniques, can also help manage gestational hypertension.
It is important for pregnant women with high blood pressure to work closely with their healthcare provider to find the most appropriate medication and lifestyle interventions for their individual situation.
Regular Prenatal Care and Monitoring
Regular prenatal care and monitoring play a crucial role in the management of gestational hypertension. Healthcare professionals closely monitor the blood pressure levels of pregnant women with this condition to detect any significant changes or complications.
In addition to monitoring blood pressure, regular prenatal care includes various interventions aimed at promoting overall maternal and fetal well-being. One essential aspect of prenatal care is providing guidance on prenatal nutrition. A balanced and nutritious diet is crucial to ensure optimal health for both the mother and the developing baby.
Additionally, healthcare providers may also recommend regular exercise during pregnancy. Engaging in moderate-intensity physical activity, with the guidance of a healthcare professional, can have numerous benefits, including improved blood pressure control and overall cardiovascular health.
It is important to note that pregnant women with gestational hypertension should always consult their healthcare provider before starting any exercise program.
Importance of Early Detection and Timely Treatment
Timely detection and treatment are crucial in ensuring the well-being of pregnant women with gestational hypertension. Early intervention plays a significant role in managing this condition and preventing potential complications. Regular prenatal care and monitoring enable healthcare providers to identify high blood pressure in pregnant women at an early stage. This allows for prompt initiation of appropriate interventions to prevent the progression of gestational hypertension and minimize the risks associated with it.
Timely treatment involves implementing various prevention strategies, such as lifestyle modifications and medication if necessary. Lifestyle modifications may include dietary changes, regular exercise, and stress reduction techniques. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to control blood pressure.
Early detection and timely treatment of gestational hypertension not only protect the health of the mother but also promote the well-being of the fetus.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can gestational hypertension be prevented?
Prevention strategies for gestational hypertension include regular prenatal care, maintaining a healthy weight, managing chronic conditions, and avoiding smoking and alcohol. Risk factors such as older age, obesity, and a history of hypertension should be closely monitored.
What are the long-term effects of gestational hypertension on the mother’s health?
The long-term implications of gestational hypertension on the mother’s health include an increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases later in life. It is important to monitor and manage blood pressure levels to mitigate this impact.
Is gestational hypertension a common condition?
The prevalence of gestational hypertension is relatively low, affecting around 6-8% of pregnancies. Risk factors include advanced maternal age, obesity, multiple pregnancies, and a history of chronic hypertension or gestational hypertension in previous pregnancies.
Can gestational hypertension affect the baby’s development?
Gestational hypertension can have an impact on the baby’s growth and development. It may result in poor fetal growth, preterm birth, or low birth weight. Proper management and monitoring by healthcare professionals are crucial to minimize these risks.
Are there any alternative therapies or treatments available for gestational hypertension?
Alternative therapies and natural remedies for gestational hypertension may include acupuncture, herbal supplements, and relaxation techniques. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before considering any alternative treatments, as their safety and effectiveness may vary.