What Is Herd Immunity and How Does It Impact Viral Spread?

The phenomenon of herd immunity, a crucial concept in public health, plays a significant role in the control and prevention of viral spread.
This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of herd immunity and its impact on viral transmission. By examining the immune system and the factors that influence herd immunity, we can shed light on the implications for public health and the importance of vaccination strategies.
Through an objective and impersonal analysis, this article seeks to elucidate the intricate relationship between herd immunity and viral spread.
Key Takeaways
- Herd immunity refers to a high proportion of immune individuals in a population and reduces the likelihood of disease spread.
- Achieving herd immunity can be challenging due to factors like vaccine effectiveness and hesitancy.
- Vaccination campaigns and public awareness are crucial for overcoming these challenges and achieving herd immunity.
- Herd immunity is crucial in preventing the spread of infectious diseases like COVID-19 and controlling viral transmission within a community.
The Concept of Herd Immunity
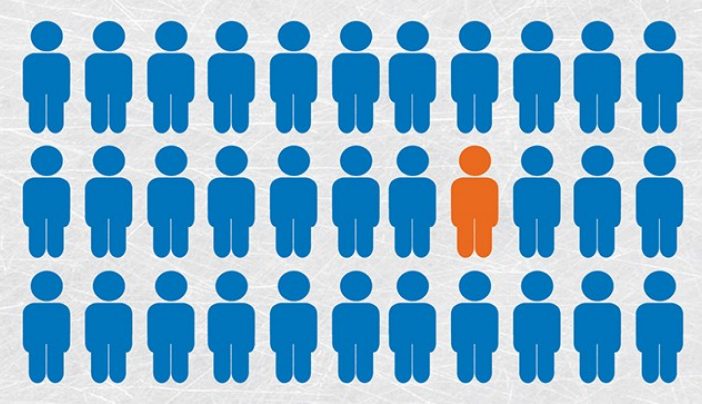
The concept of herd immunity refers to the phenomenon where a sufficiently high proportion of individuals in a population are immune to a particular infectious disease, thereby reducing the likelihood of its spread.
It is important to distinguish between herd immunity and individual immunity. While individual immunity refers to the protection of an individual against a specific pathogen, herd immunity focuses on the collective protection of a population. When a large percentage of individuals are immune, the transmission of the disease is disrupted, providing indirect protection to those who are not immune.
Achieving herd immunity can be challenging due to several factors. These include the need for a high percentage of individuals to be immune, the variability in vaccine effectiveness, the emergence of new strains, and vaccine hesitancy among certain populations.
Overcoming these challenges requires effective vaccination campaigns, public awareness, and addressing misconceptions surrounding immunization.
Understanding the Immune System
An understanding of the immune system is crucial in comprehending the mechanisms involved in protecting the body from infectious diseases. The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against harmful pathogens. When a pathogen enters the body, the immune system responds by launching an immune response. This response involves various immune cells, such as macrophages, B cells, and T cells. Macrophages engulf and destroy pathogens, while B cells produce antibodies that bind to the pathogens and mark them for destruction. T cells, on the other hand, directly attack and eliminate infected cells. The immune response is a coordinated effort that aims to eliminate the pathogen and prevent further infection.
| Immune Cells | Function |
|---|---|
| Macrophages | Engulf and destroy pathogens |
| B cells | Produce antibodies to mark pathogens for destruction |
| T cells | Directly attack and eliminate infected cells |
Factors Affecting Herd Immunity
Various factors, such as vaccination rates and the presence of susceptible individuals, can significantly influence the effectiveness of herd immunity.
Herd immunity is a crucial concept in public health, as it helps prevent the spread of infectious diseases within a population.
The size of the population plays a significant role in achieving herd immunity. The larger the population, the higher the number of individuals who need to be immune to the disease for effective herd protection.
Vaccine coverage is another critical factor in determining the success of herd immunity. The more individuals who are vaccinated against a particular disease, the greater the chances of interrupting the transmission of the pathogen within the population.
Therefore, high vaccine coverage and a large population are essential for achieving and maintaining herd immunity.
Herd Immunity and Viral Transmission
Achieving and maintaining a high level of population-wide immunity is crucial for preventing the transmission of viruses within a community. Herd immunity strategies play a significant role in controlling the spread of viral infections, including COVID-19.
The impact of herd immunity on COVID-19 can be observed through various factors:
- Vaccination campaigns: Widespread vaccination programs aim to increase the proportion of immune individuals in the population, reducing the likelihood of virus transmission.
- Natural infection: As more individuals are exposed to and recover from COVID-19, they develop immunity, contributing to the overall population-wide immunity.
- Social distancing measures: Implementing measures such as mask-wearing, hand hygiene, and maintaining physical distance can help reduce the transmission of COVID-19, thus facilitating the development of herd immunity.
Implications for Public Health and Vaccination
Public health and vaccination efforts can be informed by the implications of population-wide immunity and its role in controlling the transmission of viruses like COVID-19. Understanding the concept of herd immunity is crucial for implementing effective public health measures and maximizing vaccine effectiveness.
Herd immunity occurs when a significant proportion of the population becomes immune to a specific disease, either through vaccination or previous infection. This immunity reduces the likelihood of transmission, as the virus struggles to find susceptible individuals to infect. Consequently, public health measures can be tailored to target specific populations who have not yet achieved immunity, such as promoting vaccination campaigns or implementing social distancing measures.
Furthermore, comprehending the factors that influence vaccine effectiveness, such as the level of population immunity, can guide public health strategies to minimize the spread of diseases and protect vulnerable individuals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Herd Immunity Be Achieved Without Vaccination?
Herd immunity can potentially be achieved without vaccination through natural immunity acquired from previous infections. Alternative methods such as passive immunization or exposure to attenuated strains may also contribute to herd immunity.
How Long Does Herd Immunity Last?
The duration of herd immunity and its effectiveness vary depending on factors such as the pathogen’s characteristics, population size, and vaccination coverage. Understanding these factors can help inform public health strategies.
Can Herd Immunity Be Achieved for All Viruses?
The achievement of herd immunity for all viruses is constrained by various limitations. These include the variability of natural immunity efficacy among individuals, the emergence of viral variants, and the potential for waning immunity over time.
Are There Any Risks Associated With Relying on Herd Immunity?
Risks associated with relying on herd immunity include the potential for lower vaccine uptake, leading to incomplete protection, and the emergence of new variants that may evade immunity. Effectiveness of herd immunity depends on sufficient population coverage and vaccine efficacy.
How Does Herd Immunity Impact the Development of New Strains of Viruses?
The development of variants can be impacted by herd immunity, as it may reduce the transmission of viruses and limit their ability to mutate. The effectiveness of natural immunity in preventing variant development needs further investigation.