What Is Sleep Paralysis and How to Cope With It
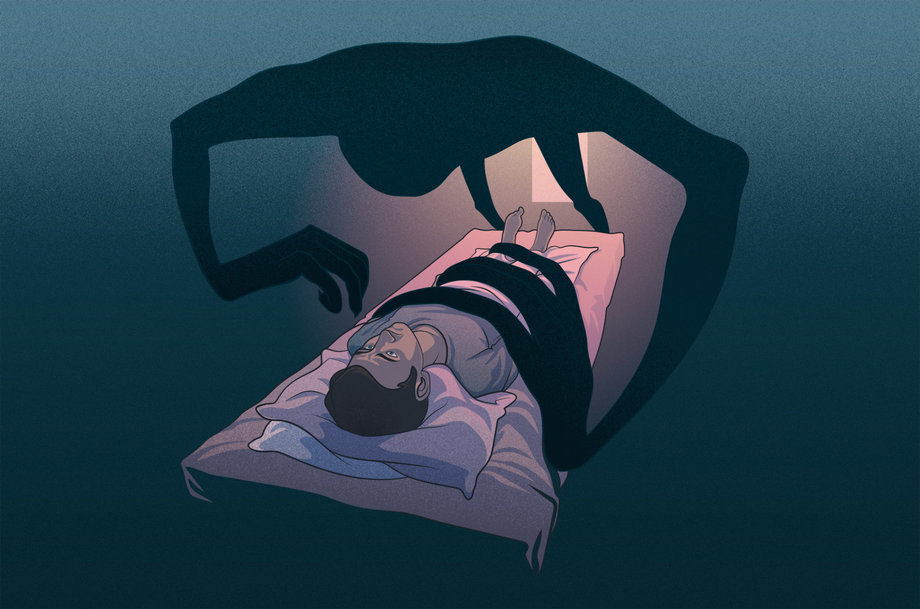

Sleep paralysis is a common phenomenon characterized by temporary immobility upon awakening or falling asleep. This condition affects a significant proportion of the population and can be distressing for those who experience it. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and experiences associated with sleep paralysis is crucial for developing effective coping strategies.
This article aims to provide an overview of sleep paralysis, explore potential coping mechanisms, and discuss the importance of seeking professional help when necessary. Additionally, preventative measures to minimize the occurrence of sleep paralysis episodes will be discussed.
Key Takeaways
- Sleep paralysis can be caused by disruptions in the sleep-wake cycle, sleep deprivation, irregular sleep patterns, psychological factors, and underlying sleep disorders.
- Terrifying hallucinations during sleep paralysis can have a negative impact on mental health, leading to anxiety, fear, and avoidance behaviors.
- Seeking medical intervention may be necessary, especially if hallucinations during sleep paralysis are distressing. Medications and cognitive-behavioral therapy can be helpful.
- Understanding the causes of sleep paralysis is important for developing effective coping strategies. Relaxation techniques, sleep hygiene, creating a relaxing sleep environment, and seeking professional help are some strategies that can be employed.
Causes of Sleep Paralysis
The causes of sleep paralysis include disruptions in the sleep-wake cycle, sleep deprivation, irregular sleep patterns, and underlying sleep disorders. Sleep paralysis is often associated with psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, and trauma. These psychological factors can contribute to the development or exacerbation of sleep paralysis.
Sleep disorders such as narcolepsy, insomnia, and sleep apnea are also commonly associated with sleep paralysis. Narcolepsy, a neurological sleep disorder characterized by excessive sleepiness and sudden loss of muscle control, is particularly linked to sleep paralysis.
Insomnia, a persistent difficulty in falling asleep or staying asleep, can disrupt the sleep-wake cycle and increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. Sleep apnea, a condition characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep, can lead to fragmented sleep and increase the risk of sleep paralysis episodes.
Overall, the causes of sleep paralysis are multifactorial, involving both psychological factors and underlying sleep disorders.
Symptoms and Signs of Sleep Paralysis
The experience of terrifying hallucinations during paralysis is a common symptom of sleep paralysis. These hallucinations often involve vivid and disturbing images, such as the presence of intruders or supernatural beings.
Given the distressing nature of these hallucinations, seeking medical intervention is necessary to alleviate the psychological impact and address any underlying sleep disorders.
Terrifying Hallucinations During Paralysis
Hallucinations experienced during sleep paralysis can be terrifying for individuals. Sleep paralysis is a phenomenon characterized by the temporary inability to move or speak while falling asleep or upon waking up. During sleep paralysis, individuals may also experience vivid hallucinations that can range from mildly unsettling to intensely frightening.
These hallucinations can be triggered by various factors such as stress, anxiety, sleep deprivation, and irregular sleep schedules. The impact of these hallucinations on mental health can be significant. Individuals may develop anxiety, fear, and avoidance behaviors due to the distressing nature of the hallucinations.
Moreover, the recurrent nature of sleep paralysis hallucinations can lead to disrupted sleep patterns and increased daytime sleepiness, further contributing to mental health issues. Understanding the triggers and seeking appropriate coping strategies can help individuals manage the impact of hallucinations during sleep paralysis on their mental well-being.
Seeking Medical Intervention Necessary
Seeking appropriate medical intervention is crucial for individuals experiencing distressing hallucinations during sleep paralysis. While sleep paralysis itself does not require treatment, the associated hallucinations can cause significant distress and may warrant medical attention.
Medical treatments for hallucinations during sleep paralysis include:
- Medications: Doctors may prescribe certain medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or benzodiazepines, to help manage the hallucinations and reduce anxiety.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): This form of therapy focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors related to sleep paralysis hallucinations. CBT can help individuals develop coping strategies and reduce anxiety.
- Sleep hygiene: Establishing a regular sleep schedule, avoiding stimulants before bed, and creating a comfortable sleep environment can help improve sleep quality and reduce the frequency of sleep paralysis hallucinations.
- Alternative therapies: Some individuals may find relief through alternative therapies such as relaxation techniques, mindfulness meditation, or hypnotherapy. While research on their effectiveness is limited, these therapies may be worth exploring for those who do not respond to traditional treatments.
It is important for individuals experiencing distressing hallucinations during sleep paralysis to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
Understanding the Sleep Paralysis Experience
This discussion aims to explore the causes of sleep paralysis and coping strategies for individuals experiencing this phenomenon.
Sleep paralysis can be caused by various factors including sleep deprivation, irregular sleep schedule, and certain sleep disorders.
Understanding the underlying causes can help individuals develop effective coping strategies such as maintaining a consistent sleep routine, managing stress levels, and seeking professional help if necessary.
Causes of Sleep Paralysis
One potential cause of sleep paralysis is disruption in the sleep-wake cycle. This disruption can be influenced by various factors, including psychological factors and the correlation between sleep paralysis and sleep disorders.
Psychological factors in sleep paralysis:
- Stress: High levels of stress can contribute to sleep disturbances and increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
- Anxiety and depression: These mental health conditions can disrupt sleep patterns and contribute to the occurrence of sleep paralysis.
- Trauma: Individuals who have experienced trauma may be more prone to sleep paralysis due to the impact it has on sleep quality.
- Sleep disorders correlation: Sleep paralysis has been linked to other sleep disorders such as narcolepsy, insomnia, and sleep apnea, indicating a potential relationship between these conditions.
Understanding the various causes of sleep paralysis can help guide interventions and coping strategies to manage this phenomenon effectively.
Coping Strategies for Sleep Paralysis
The implementation of various relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises and progressive muscle relaxation, has been suggested as a potential strategy for managing the experience of sleep paralysis. These techniques aim to promote relaxation and reduce anxiety, which may contribute to the occurrence of sleep paralysis episodes. Another effective approach for coping with sleep paralysis is cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). CBT focuses on identifying and modifying negative thought patterns and beliefs that may contribute to the experience of sleep paralysis. It may also involve techniques such as sleep hygiene education and stress management strategies. By incorporating relaxation techniques and CBT into one’s coping strategies, individuals may be able to better manage and reduce the frequency of sleep paralysis episodes.
| Relaxation Techniques | Cognitive Behavioral Therapy |
|---|---|
| Deep breathing exercises | Identifying and modifying negative thought patterns |
| Progressive muscle relaxation | Sleep hygiene education |
| Stress management strategies | Belief modification |
This table highlights some of the relaxation techniques and components of cognitive behavioral therapy that can be employed in coping with sleep paralysis.
Coping Strategies for Sleep Paralysis
Various coping strategies have been suggested for dealing with sleep paralysis. These include relaxation techniques, maintaining a regular sleep schedule, and seeking professional help if necessary.
- Relaxation techniques: Practicing relaxation techniques before bedtime can help reduce anxiety and promote a more restful sleep. Examples of relaxation techniques include deep breathing exercises or progressive muscle relaxation.
- Sleep hygiene: Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule is important in regulating sleep patterns and reducing the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day can help establish a regular sleep routine.
- Creating a relaxing sleep environment: The bedroom should be kept dark, quiet, and at a comfortable temperature. This can promote better sleep quality and decrease the chances of experiencing sleep disturbances.
- Seeking professional help: If sleep paralysis episodes are frequent, severe, or causing significant distress, it may be beneficial to seek help from a healthcare professional. A sleep specialist or therapist can provide further guidance and support in managing sleep paralysis.
Seeking Professional Help for Sleep Paralysis
Seeking assistance from healthcare professionals, such as sleep specialists or therapists, can provide individuals experiencing sleep paralysis with valuable guidance and support. Professional therapy is a recommended approach to manage sleep paralysis, as it allows individuals to explore the underlying causes of their condition and develop coping mechanisms.
Sleep specialists can conduct a thorough evaluation of the patient’s sleep patterns and provide personalized treatment plans, which may include medication or behavioral interventions. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is commonly used to address sleep-related issues and has shown promising results in reducing the frequency and severity of sleep paralysis episodes.
Additionally, alternative treatments such as relaxation techniques, mindfulness meditation, and hypnosis may also be explored under the guidance of a therapist. Collaborating with healthcare professionals can empower individuals to better understand and manage their sleep paralysis experiences, improving their overall well-being.
Preventing Sleep Paralysis Episodes
Implementing effective strategies can help reduce the frequency and intensity of episodes experienced during sleep paralysis. These strategies include:
- Relaxation Techniques: Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness meditation can help calm the mind and body before sleep, potentially reducing the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
- Sleep Hygiene: Maintaining good sleep hygiene involves establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, avoiding stimulating activities before bed, and limiting caffeine and alcohol intake. These practices can promote healthy sleep and reduce the likelihood of sleep paralysis episodes.
- Stress Management: Managing stress through techniques such as exercise, journaling, and seeking support can help reduce the occurrence of sleep paralysis. Stress reduction techniques can contribute to improved overall sleep quality.
- Sleep Position: Some individuals find that changing their sleep position can reduce the occurrence of sleep paralysis. Sleeping on the side instead of the back may be helpful for some people.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Sleep Paralysis Cause Physical Harm or Injury?
Sleep paralysis has the potential to cause physical harm or injury. It can lead to increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and feelings of suffocation, although such occurrences are rare and typically resolve on their own.
Are There Any Medications Available to Treat Sleep Paralysis?
Medications can be utilized as treatment options for sleep paralysis. It is important to consult a healthcare professional to explore potential medication choices and determine their appropriateness for addressing the symptoms of sleep paralysis.
Can Sleep Paralysis Be Hereditary?
Genetic factors play a role in the occurrence of sleep paralysis, as suggested by studies investigating its heritability. Family history of sleep paralysis has been associated with an increased risk of experiencing the condition.
Is It Possible to Experience Sleep Paralysis While Napping During the Day?
Daytime napping has been reported to increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. Individuals who engage in daytime naps may have a higher chance of encountering sleep paralysis episodes compared to those who do not nap.
Can Sleep Paralysis Be a Symptom of an Underlying Sleep Disorder?
Sleep paralysis can be a symptom of an underlying sleep disorder. Understanding the underlying causes is essential for effective treatment options. Further research is needed to fully comprehend the relationship between sleep paralysis and sleep disorders.