What Is the Connection Between Inflammation and Pain?
This article aims to examine the relationship between inflammation and pain. Specifically, it explores the role of inflammation in the generation and transmission of pain signals, as well as how chronic inflammation can lead to persistent pain.
By understanding this connection, healthcare professionals can better manage pain by addressing underlying inflammatory processes.
The objective and impersonal approach taken in this article ensures an unbiased analysis of the topic, devoid of personal pronouns.
Key Takeaways
- Inflammatory mediators sensitize nerve fibers and lower pain thresholds, enhancing the activity of pain receptors.
- Cytokines promote the dilation of blood vessels and attract immune cells to the affected area, leading to redness, warmth, swelling, and pain.
- Inflammatory mediators like prostaglandins and cytokines trigger pain signals by sensitizing pain receptors and directly stimulating them.
- Chronic inflammation can induce neuroplastic changes in the central nervous system, leading to hyperexcitability of pain pathways and the development of chronic pain conditions.
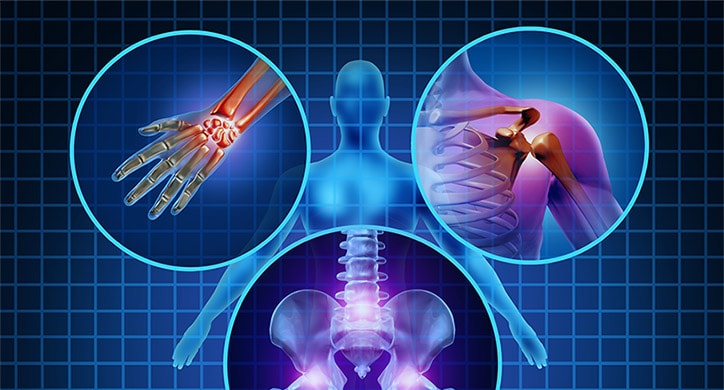
The Role of Inflammation in Pain
The role of inflammation in pain is a topic of significant interest and research in the field of physiology and pain management.
Inflammation is the body’s response to tissue damage or infection, characterized by increased blood flow, swelling, and the release of inflammatory mediators.
Inflammatory mediators, such as cytokines and chemokines, play a crucial role in modulating pain perception. They can sensitize nerve fibers, lower pain thresholds, and increase the excitability of pain signaling pathways.
Furthermore, these mediators can enhance the activity of nociceptors, which are specialized pain receptors, leading to increased pain sensitivity.
Understanding the mechanisms by which inflammatory mediators influence pain perception is essential for the development of effective pain management strategies that target inflammation-related pain conditions.
Understanding the Inflammatory Response
One of the key factors in understanding the inflammatory response is comprehending the role of cytokines in the signaling cascade.
Cytokines are small proteins that act as messengers in the immune system, playing a crucial role in the regulation of inflammation.
When tissue damage or infection occurs, immune cells release cytokines to initiate an immune response and recruit other immune cells to the site of injury or infection.
These cytokines act as inflammatory mediators, promoting the dilation of blood vessels, increasing vascular permeability, and attracting immune cells to the affected area.
This leads to the characteristic signs of inflammation, including redness, warmth, swelling, and pain.
Furthermore, cytokines also play a role in the communication between immune cells, coordinating their actions to efficiently eliminate pathogens and promote tissue repair.
Overall, understanding the role of cytokines in the signaling cascade is essential for comprehending the complex and dynamic nature of the inflammatory response.
How Inflammation Triggers Pain Signals
Understanding the mechanisms by which the inflammatory response triggers pain signals is crucial in elucidating the intricate relationship between inflammation and pain perception.
Inflammatory mediators play a pivotal role in this process. When tissue damage occurs, cells release a variety of inflammatory mediators, such as prostaglandins, bradykinin, and cytokines. These mediators act on receptors located on nerve endings, leading to the activation of pain pathways.
Prostaglandins, for example, sensitize nociceptors, making them more responsive to pain stimuli. Bradykinin, on the other hand, directly stimulates pain receptors, resulting in an immediate perception of pain. Cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta, also contribute to pain hypersensitivity.
Chronic Inflammation and Persistent Pain
Chronic inflammation is commonly associated with prolonged and continuous pain sensations. Inflammation is a natural response of the immune system to tissue damage or infection, and it is typically resolved once the underlying cause is eliminated.
However, in cases of chronic inflammation, the immune response becomes dysregulated and persists, leading to ongoing pain. The link between inflammation and pain management lies in the fact that inflammatory mediators, such as cytokines and prostaglandins, sensitize pain receptors in the affected tissues, thereby amplifying pain signals.
Moreover, chronic inflammation can also impact pain perception by inducing neuroplastic changes in the central nervous system, resulting in hyperexcitability of pain pathways. This can lead to a heightened sensitivity to pain and the development of chronic pain conditions.
Understanding the impact of chronic inflammation on pain perception is crucial for the development of effective pain management strategies in individuals with chronic inflammatory conditions.
Managing Pain by Addressing Inflammation
Addressing inflammation is a crucial aspect of managing pain in individuals with chronic inflammatory conditions. Inflammation management techniques can help reduce pain and improve overall quality of life. Here are three natural remedies for inflammation and pain:
- Diet modification: Certain foods can trigger inflammation in the body, while others have anti-inflammatory properties. Incorporating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can help reduce inflammation. Additionally, avoiding processed foods, sugary snacks, and saturated fats can also be beneficial.
- Regular exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help reduce inflammation and manage pain. Exercise promotes the release of endorphins, which are natural pain-relieving chemicals in the body. It also helps improve circulation and strengthen muscles, which can alleviate pain associated with chronic inflammatory conditions.
- Stress reduction techniques: Chronic stress can contribute to inflammation and exacerbate pain. Practicing stress reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help lower inflammation levels and provide pain relief. These techniques promote relaxation and reduce the production of stress hormones that can contribute to inflammation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Different Types of Pain Associated With Inflammation?
Differentiating acute and chronic pain is crucial in understanding the types of pain associated with inflammation. The role of inflammation in chronic pain management is an area of ongoing research and investigation.
Can Inflammation Cause Pain in Areas of the Body That Are Not Directly Affected by the Inflammatory Response?
Inflammatory mediators released during inflammation can induce pain perception not only in the affected area but also in areas not directly involved in the inflammatory response.
How Does the Body’s Immune System Respond to Chronic Inflammation?
The body’s immune system responds to chronic inflammation by activating various immune cells and releasing pro-inflammatory molecules. This immune response aims to eliminate the source of inflammation but can also contribute to tissue damage and pain.
Are There Any Natural Remedies or Lifestyle Changes That Can Help Reduce Inflammation and Alleviate Pain?
To reduce inflammation and alleviate pain, individuals can explore natural remedies and lifestyle changes. These include adopting an anti-inflammatory diet, engaging in regular exercise, managing stress levels, getting adequate sleep, and incorporating supplements like omega-3 fatty acids or turmeric.
Can Inflammation and Pain Be Completely Eliminated by Addressing the Underlying Inflammatory Condition?
The complete elimination of inflammation and pain by addressing the underlying inflammatory condition is a topic of interest. Exploring the connection between chronic inflammation and pain and the potential role of natural remedies for inflammation are areas for further investigation.