What Is The Digestive System? Common Digestive Problems And Solutions
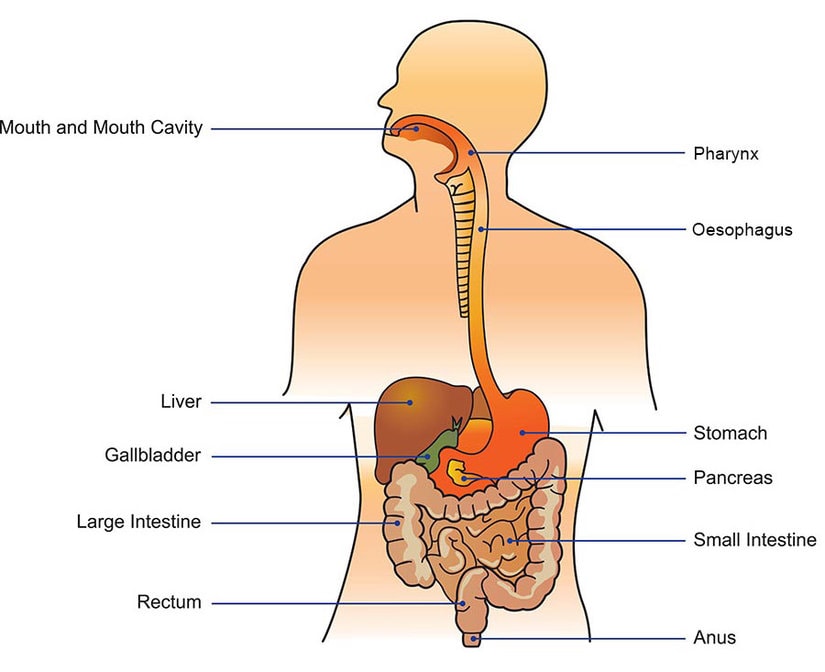
The digestive system is a complex network of organs and tissues that work together to break down food, absorb nutrients, and eliminate waste. It is essential for maintaining good health and preventing digestive problems. The digestive system begins with the mouth and ends with the anus, and includes the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
Despite its importance, the digestive system can experience a number of problems that can lead to discomfort, pain, and other health issues. These common digestive problems include heartburn and acid reflux, constipation and diarrhea, and bloating and gas.
While some of these problems can be managed with lifestyle changes, others may require medical intervention. In this article, we will explore the basics of the digestive system, the role of digestive enzymes, common digestive problems, and solutions to help you keep your digestive system healthy and functioning properly.
Key Takeaways
- The digestive system breaks down food, absorbs nutrients, and eliminates waste through organs such as the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
- Common digestive problems include heartburn, acid reflux, constipation, diarrhea, bloating, and gas, which can be caused by various factors such as diet, dehydration, lack of physical activity, and certain medications.
- Lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and medication can help manage digestive problems, but prescription medications should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider due to potential side effects.
- Improving digestive health through a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can prevent and manage digestive problems, which can impact daily activities, work, social life, and overall health.
An Overview of the Digestive System
The digestive system is a complex network of organs and tissues that work together to break down food into nutrients that can be utilized by the body.
The process of digestion begins in the mouth, where food is chewed and mixed with saliva, which contains enzymes that break down carbohydrates.
From there, the food travels down the esophagus and into the stomach, where it is mixed with stomach acid and digestive enzymes that break down proteins.
The partially digested food then moves into the small intestine, where nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream and transported to the liver for processing.
The remaining waste products move into the large intestine, where water is absorbed and solid waste is formed.
The waste products are then eliminated from the body through the rectum and anus.
The digestive system is a highly coordinated process that relies on the proper functioning of all of its components in order to work effectively.
The Role of Digestive Enzymes
One vital component in the process of breaking down food is the presence of specialized enzymes. These enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts, facilitating the chemical reactions that break down large molecules of food into smaller, more easily absorbed nutrients. Without these enzymes, the digestive process would be slow and inefficient, and our bodies would not be able to extract the vital nutrients that we need to survive.
There are several different types of digestive enzymes, each of which is specialized to break down specific types of molecules. For example, amylase is an enzyme that breaks down carbohydrates, while lipase is responsible for breaking down fats. Proteases, on the other hand, are enzymes that break down proteins. The following table provides an overview of some of the key digestive enzymes and their functions:
| Enzyme | Function |
|---|---|
| Amylase | Breaks down carbohydrates |
| Lipase | Breaks down fats |
| Proteases | Break down proteins |
| Maltase | Breaks down maltose (a type of sugar) |
| Lactase | Breaks down lactose (a type of sugar found in milk) |
By understanding the role of digestive enzymes, we can better appreciate the complex process that occurs every time we eat. Whether we are enjoying a simple snack or a full meal, our bodies rely on these enzymes to break down the food we consume and provide us with the nutrients we need to stay healthy.
Common Digestive Problems: Heartburn and Acid Reflux
Heartburn and acid reflux are conditions that can cause discomfort in the chest and throat due to the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus.
Heartburn is a burning sensation in the chest, while acid reflux is the regurgitation of food or liquid.
These conditions are common and can be caused by a variety of factors, including eating large meals, eating spicy or fatty foods, and lying down immediately after eating.
To alleviate heartburn and acid reflux, several solutions are available.
First, individuals can avoid the foods that trigger these conditions.
Second, they can eat smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day.
Third, they can avoid lying down immediately after eating and instead wait at least two to three hours before lying down.
These solutions can help alleviate the symptoms of heartburn and acid reflux and prevent them from occurring in the future.
Common Digestive Problems: Constipation and Diarrhea
Constipation and diarrhea are both uncomfortable and inconvenient conditions that can greatly affect daily life. Constipation occurs when bowel movements become difficult or infrequent, often resulting in hard, dry stools that are painful to pass. This condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including a low-fiber diet, dehydration, lack of physical activity, and certain medications. In some cases, constipation may also be a symptom of an underlying medical condition, such as irritable bowel syndrome or thyroid problems.
Diarrhea, on the other hand, is characterized by loose or watery stools that occur more frequently than usual. This condition can also be caused by a number of factors, including viral or bacterial infections, food intolerances, and certain medications. In some cases, diarrhea may be a symptom of a more serious condition, such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
Treatment for both constipation and diarrhea often involves lifestyle changes, such as increasing fiber intake, staying hydrated, and getting regular exercise. In more severe cases, medication or other medical interventions may be necessary to alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications.
Common Digestive Problems: Bloating and Gas
Bloating and gas are common symptoms experienced by many individuals, causing discomfort and embarrassment in social situations. Bloating refers to a feeling of fullness or tightness in the abdomen, often accompanied by visible swelling.
Gas, on the other hand, refers to the release of air or gases from the digestive tract, either through belching or passing gas. These symptoms can occur due to a variety of reasons, including eating certain foods, swallowing air, or underlying digestive disorders.
One common cause of bloating and gas is the consumption of foods that are difficult to digest, such as beans, lentils, and cruciferous vegetables. These foods contain complex carbohydrates that are not broken down easily by the body, leading to the production of gas in the intestines.
Other factors that can contribute to bloating and gas include eating too quickly, chewing gum, or drinking carbonated beverages. In some cases, these symptoms may also be a sign of an underlying digestive disorder, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Treatment options for bloating and gas depend on the underlying cause and may include dietary changes, probiotics, and medication.
Lifestyle Changes for Improved Digestion
Incorporating healthy lifestyle habits can have a positive impact on digestive health and overall well-being. One of the most important changes to make is to maintain a balanced and nutritious diet. This means consuming adequate amounts of fiber and water, and limiting processed and high-fat foods.
Regular exercise can also improve digestion by increasing blood flow to the digestive tract and promoting bowel regularity. Additionally, managing stress through relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help alleviate digestive symptoms and improve overall digestive health.
Other lifestyle changes that can improve digestion include getting enough sleep, chewing food thoroughly, and avoiding eating too quickly. It is also important to avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, as both can irritate the digestive system and lead to a range of digestive problems.
By adopting these healthy lifestyle habits, individuals can improve their digestive health and experience fewer digestive issues such as bloating, gas, constipation, and diarrhea. Additionally, these changes can lead to improved overall health and well-being.
Over-the-Counter and Prescription Medications
One option for managing digestive symptoms is to explore the use of over-the-counter and prescription medications, which can target specific digestive issues such as acid reflux or irritable bowel syndrome. Over-the-counter medicines include antacids, which neutralize stomach acid, and laxatives, which help relieve constipation. However, it is important to use these medications as directed and to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new medication.
Prescription medications for digestive issues may include proton pump inhibitors, which reduce the amount of acid produced in the stomach, and antibiotics, which can help treat bacterial infections in the digestive tract. Additionally, medications such as anti-diarrheals, anti-spasmodics, and anti-nausea drugs may be prescribed for specific digestive symptoms. It is important to note that some prescription medications may have side effects and should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
| Medication | Use | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Antacids | Neutralize stomach acid | May cause constipation or diarrhea |
| Laxatives | Relieve constipation | May cause cramping or dehydration |
| Proton Pump Inhibitors | Reduce stomach acid | May increase risk of bone fractures or infections |
| Antibiotics | Treat bacterial infections | May cause diarrhea or allergic reactions |
| Anti-Diarrheals | Treat diarrhea | May cause constipation or nausea |
| Anti-Spasmodics | Treat muscle spasms in the digestive tract | May cause dry mouth or blurred vision |
| Anti-Nausea Drugs | Treat nausea and vomiting | May cause drowsiness or dizziness |
Over-the-counter and prescription medications can be effective in managing digestive issues, but it is important to use them as directed and to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new medication. Additionally, some prescription medications may have side effects and should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider. Understanding the various medications available can help individuals make informed decisions about their digestive health and improve their quality of life.
When to Seek Medical Attention
After considering the available over-the-counter and prescription medications, it is important to know when to seek medical attention for digestive problems. While many digestive issues can be resolved with simple lifestyle changes or over-the-counter remedies, some may require the attention of a healthcare professional.
There are several signs that may indicate the need for medical attention when it comes to digestive problems. Here are three key things to look out for:
- Persistent symptoms: If you have been experiencing digestive issues for an extended period of time, such as weeks or months, it may be time to seek medical attention. Persistent symptoms could indicate an underlying condition that requires further investigation.
- Severe symptoms: If your symptoms are severe, such as intense pain or uncontrollable vomiting, seek medical attention immediately. These symptoms could be a signal of a serious condition that requires urgent treatment.
- New symptoms: If you experience new or unfamiliar symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional. This can help to identify any underlying conditions and ensure that appropriate treatment is given.
While over-the-counter and prescription medications can be helpful for managing digestive problems, it is important to know when to seek medical attention. Persistent or severe symptoms, as well as new symptoms, are all indications that it may be time to consult with a healthcare professional.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the digestive system plays a crucial role in breaking down food and extracting nutrients needed for the body to function properly.
Digestive enzymes play a key role in this process, and their deficiency can lead to various digestive problems like heartburn, acid reflux, constipation, diarrhea, bloating, and gas.
While lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, can help improve digestive health, over-the-counter and prescription medications may also be necessary for some individuals.
It is essential to recognize the signs of digestive problems and seek medical attention when necessary to avoid potential complications.
A healthy digestive system is vital for maintaining overall health and wellbeing.
By taking the necessary steps to improve digestive health, individuals can enjoy a better quality of life and reduce their risk of developing various health conditions associated with poor digestion.