What Is The Skeletal System? Structure, Functions, And Disorders
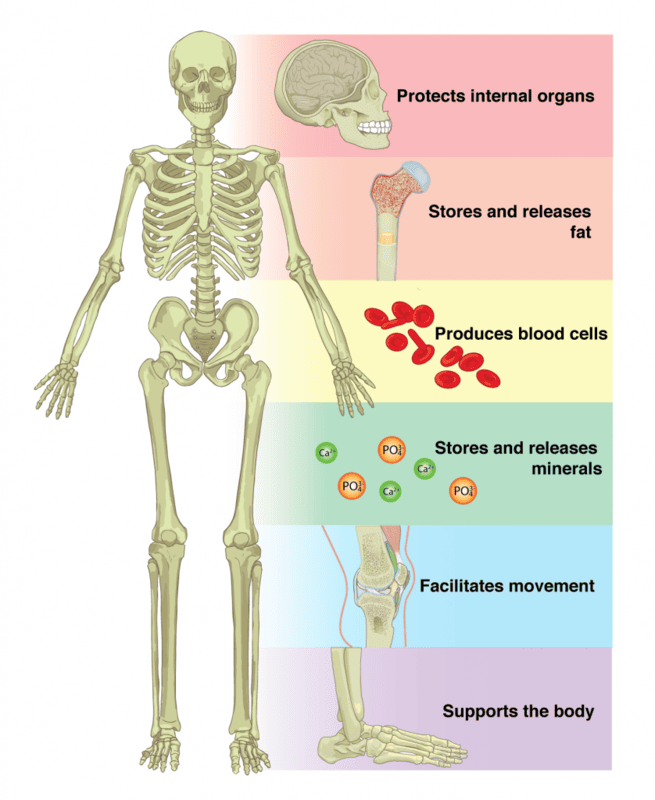
The skeletal system is a complex network of bones, cartilage, ligaments, muscles, and other supporting structures that work together to provide shape, support, and movement to the human body. It is a vital organ system that serves multiple functions, including protection of internal organs, production of blood cells, and storage of essential minerals.
The skeletal system is a dynamic structure that undergoes constant remodeling and repair, responding to various physiological and environmental stimuli.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the skeletal system, including its structure, functions, and common disorders. We will begin by discussing the building blocks of the skeletal system, including bones, cartilage, ligaments, joints, and muscles.
We will then explore the various functions of the skeletal system, including blood cell production, mineral storage, and support and movement.
Finally, we will examine some of the most common skeletal disorders, including osteoporosis, arthritis, and fractures, and discuss their causes, symptoms, treatments, and prevention strategies.
By the end of this article, readers will have a deeper understanding of the importance of the skeletal system and the role it plays in maintaining overall health and well-being.
Key Takeaways
- The skeletal system is a complex network of bones, cartilage, ligaments, muscles, and supporting structures that provides shape, support, movement, and multiple functions.
- Osteoporosis is a prevalent health concern among older adults, affecting over 10 million people in the US alone, and lifestyle changes and treatment options are available to prevent or manage it.
- Arthritis affects joints and mobility, and there are different types that can impact quality of life, but working closely with a healthcare provider to develop a tailored treatment plan is important.
- Fractures are a common condition affecting the skeletal system, and understanding causes and prevention methods can reduce the risk of injury. Treatment approaches range from immobilization to surgical intervention.
Bones: The Building Blocks of the Skeletal System
Bones, as the fundamental unit of the skeletal system, provide structural support, facilitate movement, and protect vital organs. They are composed of a hard outer layer called the cortical bone, which is responsible for providing strength and durability, and a spongy inner layer called the trabecular bone, which is responsible for storing bone marrow and facilitating the exchange of minerals. Bones are made up of a matrix of collagen and calcium phosphate crystals, which gives them their strength and rigidity.
The human body has 206 bones of various shapes and sizes, each with a specific function. For example, the long bones, such as the femur and humerus, are responsible for supporting the weight of the body and facilitating movement, while the flat bones, such as the skull and sternum, protect vital organs such as the brain and heart.
Bones also play a crucial role in the production of blood cells, as the bone marrow located in the spongy inner layer of bones is responsible for producing red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Overall, the bones of the skeletal system provide the framework for the body, allowing it to move, protect its vital organs, and maintain its overall shape and structure.
Cartilage and Ligaments: Supporting Structures
Cartilage and ligaments are essential components of the supporting structures in the human body, playing a crucial role in maintaining joint stability and enabling smooth movement.
Cartilage is a firm and flexible connective tissue that covers the ends of bones and acts as a cushioning material between them. It is made up of chondrocytes, collagen fibers, and proteoglycans, which give it its unique properties. Cartilage is found in various parts of the body, including the nose, ears, ribs, and joints.
Ligaments, on the other hand, are strong and flexible bands of tissue that connect bones to each other and provide stability to the joints. They are made up of collagen fibers and elastin, which allow them to stretch and contract. Ligaments are found in various parts of the body, including the knee, ankle, wrist, and spine. They play a critical role in preventing excessive movement of the joints, which can lead to injury or damage.
Overall, cartilage and ligaments work together to provide support and stability to the body, allowing for smooth and efficient movement.
Joints and Muscles: Enabling Movement
The intricate coordination of joints and muscles is a complex process that enables the human body to move with precision and grace. Joints are the meeting points between bones, and they allow for movement and flexibility. There are several types of joints in the body, including hinge, ball-and-socket, and pivot joints. Each type of joint has a unique structure that allows for specific movements. For example, the hinge joint found in the elbow and knee only allows for bending and straightening, while the ball-and-socket joint in the hip and shoulder allows for a greater range of motion in all directions.
Muscles are responsible for moving the body by contracting and relaxing. They work in pairs, with one muscle contracting while the other relaxes, allowing for movement in opposite directions. There are three types of muscles in the body: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscles are the largest and most visible, and they attach to bones through tendons. They are responsible for voluntary movements, such as walking and lifting weights. Smooth muscles are found in the walls of internal organs, such as the stomach and intestines, and they are responsible for involuntary movements, such as digestion. Cardiac muscle is found only in the heart and is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. The intricate interplay between joints and muscles allows for the complex movements that the human body is capable of, but it is also the source of many common disorders, such as arthritis and muscle strains.
| Joint Type | Example | Structure | Movement | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hinge | Elbow, knee | Two bones with a strong ligament connecting them | Bending and straightening | |||||
| Ball-and-socket | Hip, shoulder | A ball-shaped bone fitting into a socket-shaped bone | Movement in all directions | |||||
| Pivot | Neck, forearm | A ring of bone and a bone that rotates within it | Rotation around a central axis | Hinge | Elbow, knee | Two bones joined together with a hinge-like joint | Movement in one direction, like a door hinge |
Bone Marrow: Blood Cell Production
Bone marrow is responsible for the production of all types of blood cells in the body. It is a spongy tissue found inside the bones, particularly in the hip and thigh bones, sternum, and vertebrae.
The bone marrow contains stem cells, which are immature cells that can develop into different types of blood cells. These stem cells undergo a process called hematopoiesis, which involves the formation and differentiation of the stem cells into red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
The process of hematopoiesis is regulated by several factors, including hormones and growth factors.
The bone marrow is essential for the proper functioning of the immune system, as it produces white blood cells that help fight infections and diseases. It also plays a crucial role in the formation of red blood cells, which are responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body.
Additionally, platelets produced by the bone marrow are necessary for blood clotting, which helps prevent excessive bleeding.
Disorders that affect the bone marrow, such as leukemia and aplastic anemia, can result in a decrease in the production of blood cells, leading to a weakened immune system, anemia, and bleeding disorders.
Calcium and Phosphorus: Essential Minerals
Calcium and phosphorus are crucial minerals that play a vital role in maintaining strong and healthy bones, and their deficiency can lead to significant health problems.
Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body, and it is primarily found in bones and teeth. It is essential for muscle contraction, nerve function, blood clotting, and the release of hormones and enzymes. The body needs a constant supply of calcium to maintain these functions, and if it does not get enough calcium from the diet, it will start to leach calcium from bones, which can weaken them over time.
Phosphorus is another essential mineral that is closely linked to calcium. It is also found in bones and teeth, and it is involved in many of the same functions as calcium. In addition, phosphorus is a key component of DNA and RNA, the building blocks of life.
The body tightly regulates the levels of calcium and phosphorus in the blood, and they work together to maintain a healthy balance. If there is an imbalance between these minerals, it can lead to bone loss, weakened teeth, muscle weakness, and other health problems.
Therefore, it is important to consume a balanced diet that includes adequate amounts of calcium and phosphorus to support bone health and overall wellbeing.
Osteoporosis: A Common Skeletal Disorder
Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by low bone density and increased risk of fractures, is a prevalent health concern among older adults. It is estimated that over 10 million people in the United States alone suffer from osteoporosis, with women being more prone to the condition than men. Osteoporosis occurs when the body fails to produce enough new bone or when too much old bone is absorbed by the body.
As a result, bones become weak and brittle, making them more susceptible to fractures. To prevent or manage osteoporosis, individuals should incorporate certain lifestyle changes and treatment options. These include:
- A well-balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D
- Regular exercise, particularly weight-bearing and resistance training
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Medications such as bisphosphonates, hormone therapy, and calcitonin
- Fall prevention strategies, such as removing trip hazards and using assistive devices as needed.
By implementing these strategies, individuals can reduce their risk of developing osteoporosis or improve their quality of life if they have already been diagnosed with the condition.
Arthritis: Affecting Joints and Mobility
Arthritis is a debilitating condition that affects the joints, causing pain and limiting mobility, and is a common health concern among older adults. It is characterized by inflammation, swelling, stiffness, and pain in one or more joints of the body.
There are many different types of arthritis, with osteoarthritis being the most common. Other types include rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and gout. The exact cause of arthritis is still unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
Arthritis can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life, making it difficult to perform daily tasks and participate in activities they enjoy. Treatment options for arthritis include medication, physical therapy, exercise, and surgery.
Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking can also help manage symptoms. It is important for individuals with arthritis to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to their specific needs and goals.
With proper management, many individuals with arthritis are able to live active and fulfilling lives.
Fractures: Types, Treatment, and Prevention
Arthritis, as discussed in the previous subtopic, is a common disorder affecting the joints and mobility. However, another common condition that affects the skeletal system is fractures. Fractures refer to a break or crack in one or more bones of the body. It is a prevalent injury, especially among athletes and those involved in physical activities.
There are various types of fractures, each with different treatment approaches and prevention methods. The type of fracture depends on the location, severity, and cause of the injury. Treatment could range from immobilization of the affected area to surgical intervention. Prevention methods include wearing protective gear during physical activities, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and avoiding risky behaviors. The following table provides a summary of different types of fractures, their causes, treatment, and prevention methods.
| Type of Fracture | Causes | Treatment | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stress Fracture | Overuse or repetitive stress | Rest, ice, and pain medication | Gradual increase in exercise and proper footwear |
| Open Fracture | Bone breaks through the skin | Surgery, antibiotics, and wound care | Protective gear and safe behaviors |
| Comminuted Fracture | Bone breaks into several pieces | Surgery or immobilization | Protective gear and safe behaviors |
| Greenstick Fracture | Incomplete break in a bone | Immobilization | Protective gear and safe behaviors |
| Hairline Fracture | Tiny crack in a bone | Rest, ice, and pain medication | Gradual increase in exercise and proper footwear |
Fractures are a common injury affecting the skeletal system. The type of fracture determines the treatment and prevention methods. Preventive measures such as wearing protective gear and avoiding risky behaviors can reduce the risk of fractures. Understanding the various types of fractures and their causes is crucial in preventing and managing this condition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the skeletal system is a complex and vital part of the human body. It is made up of bones, cartilage, ligaments, joints, and muscles, all working together to provide support, movement, and protection.
Bone marrow produces blood cells, while calcium and phosphorus are essential minerals for bone health. However, the skeletal system is also susceptible to disorders such as osteoporosis, arthritis, and fractures.
Osteoporosis is a common disorder that weakens bones, increasing the risk of fractures. Arthritis affects joints, causing pain and stiffness that can limit mobility. Fractures can occur due to trauma or weakened bones and require proper treatment and prevention measures.
It is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption to keep the skeletal system strong and healthy. Understanding the skeletal system and its disorders can help individuals take steps to prevent and treat skeletal issues.