Why Hypertension Is Related To Peripheral Artery Disease?
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a significant global health issue with implications for various cardiovascular diseases. One such disease closely associated with hypertension is peripheral artery disease (PAD).
This article aims to explore the link between hypertension and PAD, including the underlying mechanisms and shared risk factors. Additionally, it will discuss the common symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options for both conditions.
Lifestyle modifications and the importance of regular monitoring and follow-up care will also be highlighted. The objective of this article is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the relationship between hypertension and PAD, considering the current research and advancements in treatment.
By examining this connection, healthcare professionals and individuals can better comprehend the implications of hypertension on the development and management of PAD, ultimately leading to improved prevention and treatment strategies.
Key Takeaways
- Hypertension management involves dietary changes, exercise, regular monitoring, and follow-up care.
- Consistent healthcare management, including regular check-ups and medication management, can lead to early detection of complications, optimal blood pressure control, identification of medication side effects, improved adherence to treatment plans, and reduced risk of peripheral artery disease.
- Advancements in medical research have resulted in innovative treatment options for hypertension and peripheral artery disease, such as ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, and statins.
- Medications and lifestyle modifications have significantly improved outcomes and quality of life for patients with hypertension and peripheral artery disease.
Understanding Hypertension and its Effects on the Arteries
Hypertension, characterized by persistently elevated blood pressure, plays a significant role in the development and progression of peripheral artery disease due to its detrimental effects on arterial structure and function. Understanding hypertension and its impact on arterial health is crucial in comprehending the relationship between hypertension and peripheral artery disease.
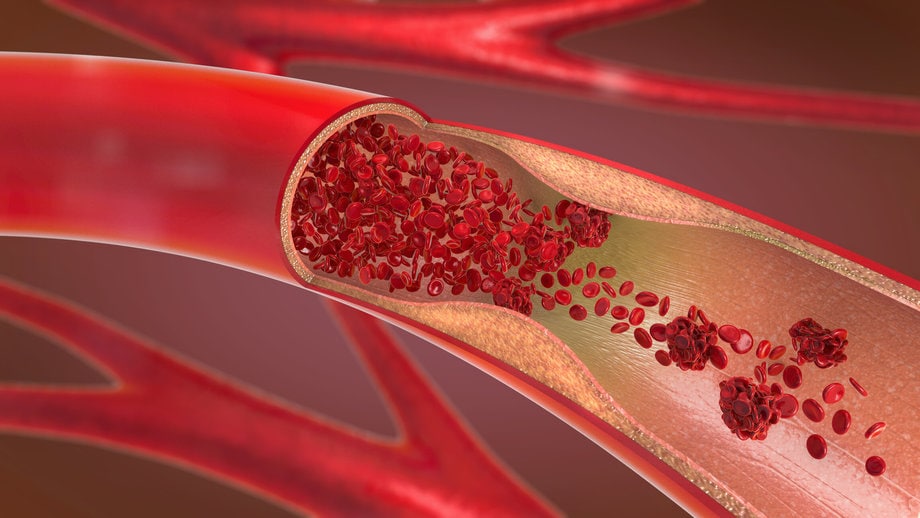
Hypertension exerts excessive force on the arterial walls, leading to endothelial dysfunction and impaired vasodilation. The persistent high pressure damages the endothelial cells, resulting in inflammation, oxidative stress, and impaired nitric oxide production. These changes contribute to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques within the arteries.
Moreover, hypertension promotes arterial stiffness, reducing their ability to expand and accommodate blood flow, further compromising peripheral circulation. The combination of endothelial dysfunction, atherosclerosis, and arterial stiffness caused by hypertension creates an unfavorable environment for peripheral artery health.
These alterations disrupt the normal blood flow to peripheral tissues, leading to ischemia, pain, and ultimately peripheral artery disease. Therefore, understanding the intricate relationship between hypertension and arterial health is essential in elucidating the mechanisms underlying the development and progression of peripheral artery disease.
The Link Between Hypertension and Peripheral Artery Disease
The elevated blood pressure commonly associated with this condition has been found to be strongly correlated with the development and progression of vascular complications in the extremities. Understanding this link between hypertension and peripheral artery disease (PAD) is crucial for effective prevention and management strategies.
Here are three key points to consider:
- Hypertension and PAD prevention: Managing hypertension is essential in preventing the development of PAD. By controlling blood pressure levels within a normal range, the risk of vascular complications in the extremities can be significantly reduced.
- Managing hypertension and PAD through medication: Medication plays a vital role in managing hypertension and preventing or slowing down the progression of PAD. Anti-hypertensive drugs, such as ACE inhibitors or calcium channel blockers, help lower blood pressure and improve blood flow to the extremities.
- Importance of lifestyle modifications: Alongside medication, lifestyle modifications are crucial in managing hypertension and PAD. This includes adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight.
By understanding the relationship between hypertension and PAD and implementing appropriate prevention and management strategies, individuals can reduce the risk of vascular complications and improve their overall cardiovascular health.
Risk Factors for Developing Hypertension and PAD
Risk factors, such as age, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle, have been identified as significant contributors to the development of both high blood pressure and vascular complications in the extremities. Hypertension and peripheral artery disease (PAD) share common risk factors and pathophysiological mechanisms. Prevention strategies targeting these risk factors can help reduce the incidence of both conditions.
Aging is a major risk factor for both hypertension and PAD, with the prevalence increasing with age.
Obesity, characterized by excessive body fat, is strongly associated with hypertension and PAD due to the increased strain on the cardiovascular system.
Furthermore, a sedentary lifestyle, characterized by physical inactivity, is a modifiable risk factor that contributes to the development of both hypertension and PAD.
It is important to address these risk factors in order to prevent the long-term complications associated with hypertension and PAD.
Common Symptoms of Hypertension and PAD
A better understanding of the common symptoms experienced by individuals with high blood pressure and vascular complications in the extremities can elicit a sense of urgency in addressing these conditions.
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, and peripheral artery disease (PAD) often coexist, sharing similar risk factors and pathophysiological mechanisms.
Common symptoms of hypertension include headaches, dizziness, chest pain, and shortness of breath.
On the other hand, PAD is characterized by symptoms such as leg pain, cramping, numbness, and weakness, especially during physical activity.
The connection between hypertension and PAD lies in the fact that both conditions can lead to atherosclerosis, a narrowing and hardening of the arteries.
This can result in reduced blood flow to the extremities, causing symptoms associated with PAD.
Understanding this connection is crucial for early detection and management of these conditions to prevent further complications and improve patient outcomes.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Hypertension and PAD
Diagnosis of hypertension and PAD involves a combination of medical history, physical examinations, and diagnostic tests.
To diagnose hypertension, healthcare professionals typically measure blood pressure levels using a sphygmomanometer. Additionally, they may request blood tests to assess kidney function and levels of cholesterol and glucose.
For PAD, physical examinations may include checking for weak or absent pulses in the limbs, listening for abnormal sounds in the arteries, and assessing skin color and temperature. Diagnostic tests such as ankle-brachial index, Doppler ultrasound, and angiography are also commonly used.
Treatment advancements for hypertension and PAD aim to manage symptoms, reduce the risk of complications, and improve overall quality of life. Lifestyle modifications, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, are often recommended. Medications, such as antihypertensives and antiplatelet agents, may be prescribed. In severe cases, surgical procedures like angioplasty or bypass surgery may be necessary.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Hypertension and Reduce the Risk of PAD
To effectively manage high blood pressure and reduce the likelihood of developing peripheral arterial disease, individuals should adopt healthy lifestyle changes that prioritize regular exercise and a balanced diet.
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing hypertension, as they can help lower blood pressure levels and improve overall cardiovascular health. Engaging in regular physical activity, such as aerobic exercises and strength training, can help reduce blood pressure and improve blood flow.
Additionally, a balanced diet that is low in sodium, saturated fats, and cholesterol can further aid in blood pressure management. It is also important to maintain a healthy body weight and limit alcohol consumption.
In some cases, medication management may be necessary to control hypertension. Working in collaboration with healthcare professionals, individuals can develop a personalized treatment plan that includes lifestyle modifications and, if needed, appropriate medications to effectively manage hypertension and reduce the risk of peripheral arterial disease.
The Importance of Regular Monitoring and Follow-Up Care
Regular monitoring and follow-up care are essential for effectively managing high blood pressure and reducing the risk of developing complications. Regular check-ups allow healthcare professionals to assess the effectiveness of hypertension treatment and make necessary adjustments to medication management. Monitoring blood pressure levels helps identify any fluctuations or spikes that may require immediate attention. Additionally, regular follow-up visits provide an opportunity to discuss lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and exercise routines, which can contribute to better blood pressure control.
To further emphasize the importance of regular monitoring and follow-up care, a table can be included to highlight the benefits and outcomes associated with consistent healthcare management. This table could include columns such as “Regular Check-ups” and “Medication Management,” and rows could include “Early detection of complications,” “Optimal blood pressure control,” “Identification of medication side effects,” “Improved adherence to treatment plan,” and “Reduced risk of peripheral artery disease.” By visually presenting these benefits, the audience can better understand the significance of regular monitoring and follow-up care in hypertension management.
| Regular Check-ups | Medication Management |
|---|---|
| Early detection of complications | Optimal blood pressure control |
| Identification of medication side effects | Improved adherence to treatment plan |
| Reduced risk of peripheral artery disease |
Research and Advancements in Hypertension and PAD Treatment
Advancements in medical research have led to innovative treatment options for managing and improving outcomes in both hypertension and peripheral artery disease (PAD).
Research advancements have identified several medication options that can effectively control hypertension and alleviate symptoms of PAD. One such medication is ACE inhibitors, which work by relaxing blood vessels and reducing blood pressure.
Another medication option is calcium channel blockers, which also help relax blood vessels and improve blood flow. Additionally, research has shown that statins, commonly prescribed for high cholesterol, can also benefit individuals with PAD by reducing inflammation and improving blood flow.
These medication options, along with lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise and a healthy diet, have significantly improved the management of hypertension and PAD, leading to better outcomes and a higher quality of life for patients.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of hypertension?
Hypertension can be classified into primary and secondary types. Primary hypertension, also known as essential or idiopathic hypertension, has no identifiable cause. Secondary hypertension, on the other hand, is caused by an underlying medical condition or medication use.
Can peripheral artery disease be prevented?
Prevention strategies for peripheral artery disease (PAD) include lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and controlling diabetes.
How is hypertension diagnosed?
Diagnosis of hypertension involves various methods, including blood pressure measurements. It is essential to accurately measure blood pressure multiple times to confirm a diagnosis and assess the severity of hypertension.
Are there any natural remedies for managing hypertension and PAD?
Some natural remedies for managing hypertension and PAD include lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet, quitting smoking, and reducing stress levels.
What are the long-term complications of hypertension and PAD if left untreated?
The long-term consequences of untreated hypertension and PAD include an increased risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attack and stroke, as well as complications such as kidney disease and peripheral neuropathy. These health risks highlight the importance of managing both conditions.