Apolipoprotein B (Apob) Test Explained: What Is It For?
The Apolipoprotein B (Apob) test is a simple blood test that assesses an individual’s risk of cardiovascular disease and metabolic disorders.
It provides valuable information about cholesterol management and helps doctors guide patients towards lifestyle modifications for improved health.
Key Takeaways
- Apolipoprotein B (Apob) is a protein involved in cholesterol and fat transport in the body, playing a crucial role in maintaining a healthy lipid profile.
- Measuring Apob levels provides a more accurate assessment of cardiovascular risk compared to LDL cholesterol alone.
- High levels of Apob indicate an increased risk of heart disease, making the Apob test a useful tool in evaluating cardiovascular disease risk.
- Lifestyle modifications, such as dietary interventions and exercise, can help improve Apob levels and reduce the risk of metabolic disorders.
What Is Apolipoprotein B (Apob)?
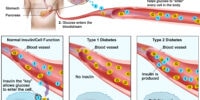
Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) is a crucial protein involved in the transport of cholesterol and other fats in the body. Its functions are vital for maintaining a healthy lipid profile and preventing cardiovascular diseases. ApoB plays a significant role in the relationship between cholesterol and heart health. It’s responsible for the packaging and transportation of cholesterol from the liver to other parts of the body.
ApoB measurement is of utmost significance in assessing the risk of developing heart disease. High levels of ApoB indicate an increased risk, as it’s associated with elevated levels of LDL cholesterol, commonly known as ‘bad’ cholesterol.
The measurement of ApoB can provide a more accurate assessment of cardiovascular risk compared to measuring LDL cholesterol alone. ApoB reflects the total number of atherogenic lipoproteins in the blood, including LDL particles. As a result, it provides a better evaluation of the overall cholesterol burden in the body.
Monitoring ApoB levels is crucial in the management of dyslipidemia and guiding treatment decisions. By targeting ApoB levels, healthcare professionals can tailor interventions to reduce cardiovascular risk effectively. Lifestyle modifications, such as adopting a healthy diet and increasing physical activity, can help lower ApoB levels and improve heart health. Additionally, medication management may be necessary to achieve optimal ApoB levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.
How Is the Apob Test Conducted?
To understand how the ApoB test is conducted, it’s important to know the steps involved in measuring this crucial protein’s levels in the body.
The ApoB test procedure begins with a blood sample typically taken from a vein in your arm. The sample requirements are usually minimal, with only a small amount of blood needed for analysis. Once the sample is collected, it’s sent to a laboratory where it undergoes analysis to determine the levels of apolipoprotein B.
The test accuracy of the ApoB test is generally considered to be high. It provides valuable information about your risk for cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attacks and strokes. However, it’s important to note that the accuracy of the test may vary depending on the laboratory and the specific method used for analysis.
Cost considerations may also come into play when considering the ApoB test. The cost of the test can vary depending on factors such as the location, healthcare provider, and insurance coverage. It’s advisable to check with your healthcare provider or insurance company to understand the potential costs associated with the ApoB test.
While the ApoB test is a valuable tool for assessing cardiovascular risk, it does have potential limitations. It’s important to remember that the test measures the levels of apolipoprotein B, but it doesn’t provide a complete picture of your overall cardiovascular health. Other factors, such as lifestyle choices and genetic predisposition, also play a significant role in determining your risk for cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, it’s important to interpret the results of the ApoB test in conjunction with other clinical and lifestyle factors to make informed decisions about your health.
Understanding the Role of Apob in Cholesterol Management
Managing cholesterol levels is crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health. Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) plays an essential role in cholesterol management. Your diet plays a significant role in ApoB levels. Foods high in saturated and trans fats can increase ApoB levels, leading to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. On the other hand, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help lower ApoB levels and promote heart health.
Inflammation also affects ApoB levels. Chronic inflammation in the body can lead to an increase in ApoB, contributing to the development of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and stress management, can help reduce inflammation and keep ApoB levels in check.
Genetic factors can also influence ApoB levels. Certain genetic variations can lead to higher ApoB levels, even in individuals with a healthy lifestyle. Understanding your genetic predisposition can help you make informed decisions about your diet, exercise, and medication choices to manage ApoB levels effectively.
It is also important to be aware of medication interactions that can affect ApoB levels. Some medications, such as statins, can lower ApoB levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events. However, other medications, like certain diuretics and beta-blockers, may increase ApoB levels. Discussing your medications with your healthcare provider can help you understand how they may impact your ApoB levels.
Apob Test and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Assessment
Assessing your risk of cardiovascular disease can be done through the Apob Test. This test is used to evaluate your cardiovascular risk by measuring the levels of apolipoprotein B (Apob) in your blood sample. Apob is a protein that is found in low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL), which are responsible for transporting cholesterol in the bloodstream.
The Apob Test is a valuable tool in determining your cardiovascular risk because it provides information about your lipid profile, specifically your cholesterol levels. High levels of Apob indicate a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, as it suggests that there is an excessive amount of LDL and VLDL in your blood. This can lead to the buildup of plaques in the arteries, increasing the likelihood of heart attacks and strokes.
It is important to note that while the Apob Test can provide valuable information about your cardiovascular risk, it is not the only factor to consider. Other factors, such as lifestyle choices, family history, and genetic factors, also play a role in determining your risk. However, the Apob Test can be a useful tool in conjunction with these other factors to assess your overall risk of cardiovascular disease.
To help you understand the significance of the Apob Test in cardiovascular risk evaluation, here is a table summarizing the different levels of Apob and their corresponding risk levels:
| Apob Level | Risk Level |
|---|---|
| Below 90 mg/dL | Low risk |
| 90-110 mg/dL | Intermediate risk |
| Above 110 mg/dL | High risk |
The Connection Between Apob and Metabolic Disorders
The relationship between Apob and metabolic disorders is a crucial aspect to understand in assessing cardiovascular risk. Apob, a protein found in certain lipoproteins, plays a significant role in the development of metabolic disorders such as obesity, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, liver disease, and atherosclerosis.
Firstly, Apob and obesity are closely linked. High levels of Apob in the blood can contribute to the accumulation of excess fat, leading to obesity. This excess fat, especially around the abdominal area, is associated with an increased risk of metabolic disorders.
Secondly, Apob is also connected to insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells don’t respond properly to insulin. Elevated levels of Apob can impair insulin signaling, leading to insulin resistance and the subsequent development of type 2 diabetes.
Furthermore, Apob plays a role in liver disease, as it’s involved in the production and transport of liver lipids. Abnormal Apob levels can contribute to the accumulation of fat in the liver, leading to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and potentially progressing to more severe liver conditions.
Lastly, Apob is a key player in atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries. Apob-containing lipoproteins, such as LDL cholesterol, can penetrate the arterial wall, triggering an inflammatory response and the formation of plaque.
When and Why Would a Doctor Order an Apob Test?
If you are experiencing symptoms or have risk factors for metabolic disorders, your doctor may order an Apob test to assess your cardiovascular health. An Apob test measures the levels of apolipoprotein B, a protein that is found in low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles. High levels of Apob are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. Here are some reasons why a doctor may order an Apob test:
| When and Why Would a Doctor Order an Apob Test? |
|---|
| If you are experiencing symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or swelling in the legs, your doctor may order an Apob test to check for high Apob levels. |
| If you have risk factors for metabolic disorders, such as obesity, diabetes, or a family history of cardiovascular diseases, your doctor may order an Apob test as a preventive measure. |
| If you are taking medication for cholesterol management, such as statins, your doctor may order an Apob test to monitor the effectiveness of the medication in lowering Apob levels. |
Untreated high Apob levels can lead to various complications, including atherosclerosis, heart attack, and stroke. Therefore, early detection through an Apob test can help prevent these complications and guide appropriate treatment. Additionally, incorporating Apob testing in preventive healthcare can help identify individuals at risk and provide interventions to reduce their cardiovascular risk. Despite the potential benefits, it is important to consider the cost effectiveness of Apob testing, especially in individuals without symptoms or risk factors. Discuss with your doctor to determine if an Apob test is appropriate for you.
Interpreting Apob Test Results and Their Significance
To interpret Apob test results and understand their significance, you need to consider the levels of apolipoprotein B in your blood. The Apob test measures the amount of Apob, a protein found in low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles, in your bloodstream.
Interpreting the results involves comparing your levels to the reference ranges provided by the laboratory. If your levels are within the normal range, it suggests that your LDL cholesterol levels are under control, reducing your risk of cardiovascular diseases. On the other hand, if your levels are high, it may indicate an increased risk of heart disease and other related conditions.
When interpreting the results, it’s important to consider potential causes for elevated Apob levels, such as obesity, diabetes, and hereditary conditions. Additionally, the clinical implications of the results should be taken into account, as high levels may warrant further testing and medical intervention. Your healthcare provider may recommend lifestyle modifications, such as a healthy diet and exercise, or prescribe medications to help lower your LDL cholesterol levels.
Lifestyle Modifications to Improve Apob Levels and Overall Health
Consider incorporating lifestyle modifications to improve your Apob levels and overall health. Making changes to your diet, exercise routine, and weight management strategies can have a positive impact on your Apob levels.
- Dietary interventions: A healthy, balanced diet is essential for managing Apob levels. Incorporate more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your meals. Limit your intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol-rich foods. Opt for healthier cooking methods such as grilling or baking instead of frying.
- Exercise recommendations: Regular physical activity can help improve your Apob levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise each week. Include activities that raise your heart rate and strengthen your muscles. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the right exercise plan for you.
- Weight management strategies: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing Apob levels. If you’re overweight or obese, losing even a small amount of weight can make a significant difference. Focus on portion control, mindful eating, and incorporating regular physical activity into your routine.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are There Any Risks or Side Effects Associated With the Apob Test?
You may experience some risks or side effects associated with the Apob test. Make sure to discuss potential complications with your doctor, who can provide more personalized information based on your medical history.
How Long Does It Typically Take to Receive the Results of an Apob Test?
It typically takes a few days to receive the results of an Apob test. Once the turnaround time is complete, you will be notified of your results. It’s important to accurately interpret the results and take any necessary follow-up actions based on the test accuracy.
Can the Apob Test Be Used to Diagnose Specific Cardiovascular Diseases?
Sure, the Apob test can help diagnose specific cardiovascular diseases. But don’t rely solely on it. Its diagnostic accuracy is being debated. Consider alternative tests, research studies, patient education, and treatment options for a comprehensive approach.
Are There Any Specific Medications or Dietary Restrictions That Need to Be Followed Before Taking the Apob Test?
Before taking the Apob test, remember to follow medication and dietary restrictions as instructed by your healthcare provider. It is also important to fast for a certain period of time to ensure accurate test results and avoid potential interactions.
Is the Apob Test Covered by Insurance?
Insurance coverage for the Apob test varies. It’s important to check your plan’s coverage details, reimbursement policies, and any preauthorization requirements. Consider costs, affordability, and potential out-of-pocket expenses before proceeding with the test.