Blood Donor Eligibility: Who Can Donate And Who Cannot
Blood donation is an essential aspect of healthcare, as it helps to replenish the blood supply for patients who require transfusions due to injuries, surgeries, or medical conditions. However, not everyone is eligible to donate blood due to various factors that may affect the safety and reliability of the blood supply.
Understanding the criteria for blood donor eligibility is crucial for ensuring that the donated blood is safe and effective for patients in need. This article aims to provide an overview of the eligibility requirements for blood donation, including age restrictions, weight limitations, health conditions, medications, lifestyle factors, and travel restrictions.
By understanding the factors that may affect eligibility, potential donors can determine whether they meet the criteria for blood donation and help to ensure the safety and availability of the blood supply for those in need.
Key Takeaways
- Age eligibility varies by country, with a minimum age of 16 years old with parental consent or 17 years old without consent.
- Donors must meet body mass index requirements and may be disqualified if they have anemia or certain infections, take certain medications, or engage in high-risk behaviors.
- There are travel restrictions in place to prevent transmission of infectious diseases, and donors must disclose their travel history to determine eligibility.
- The screening process includes a questionnaire, physical exam, and lab testing, and donors must provide accurate medical history. Hemoglobin levels may also impact eligibility.
Age Requirements for Blood Donation
Age eligibility is a crucial aspect of blood donation, as individuals must meet the minimum age requirement of 16 years old with parental consent or 17 years old without consent to qualify as a donor. This requirement ensures that donors have reached a certain level of maturity and responsibility before donating blood. Additionally, age limits also help to minimize the risk of health complications that may arise during or after the donation process.
While age eligibility may seem straightforward, it is important to note that different countries may have varying age requirements for blood donation. For example, some countries may require donors to be at least 18 years old, while others may allow individuals as young as 15 years old to donate with parental consent.
Regardless of the specific age limit, it is essential for potential donors to check with their local blood donation centers to ensure that they meet the age requirements before attempting to donate blood.
Weight Restrictions for Donors
Body mass index (BMI) is a common measure used to determine if a person meets weight requirements for blood donation, with a minimum BMI of 18.5 and a maximum of 30.0. This is because a person’s weight can greatly affect their ability to donate blood safely.
Here are some key points to consider regarding weight restrictions for blood donors:
- Donors who weigh less than 110 pounds are generally not eligible to donate blood, as the amount of blood collected during a donation can be harmful to their health.
- Donors who weigh over 350 pounds may also be ineligible to donate blood, as their weight can make it difficult to find a vein and safely collect blood.
- Donors who are pregnant or have recently given birth may be subject to weight restrictions as well, as their bodies may not be able to handle the stress of blood donation.
Overall, weight restrictions for blood donation are in place to ensure the safety and well-being of both the donor and the recipient. If you are unsure if you meet weight requirements for blood donation, it is best to consult with a healthcare professional before attempting to donate.
Health Conditions That May Affect Eligibility
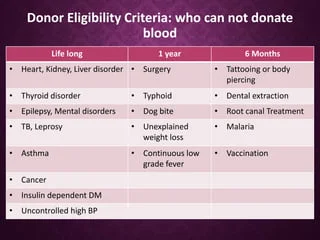
Various health conditions may impact an individual’s ability to safely donate blood. One of the most common health conditions that may affect eligibility is anemia. Anemia is a condition characterized by a lack of red blood cells or hemoglobin in the blood, which can result in fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
Individuals with anemia may not be able to donate blood because their body may not be able to tolerate the loss of red blood cells during the donation process. However, some types of anemia, such as iron-deficiency anemia, may be treated with supplements, and individuals with this type of anemia may be eligible to donate blood.
Other health conditions that may impact eligibility include certain infections, such as HIV, hepatitis B and C, and malaria. Individuals who have been diagnosed with these infections are not eligible to donate blood because there is a risk of transmitting the infection to the recipient. Additionally, individuals with a history of certain cancers, such as leukemia and lymphoma, may not be eligible to donate blood.
It is important for individuals to disclose any health conditions or medications they are taking to the blood donation center staff to determine their eligibility to donate blood.
Medications That May Disqualify Donors
Certain medications may render individuals ineligible to donate blood due to potential adverse effects on the recipient. These medications include antibiotics, anti-platelet agents, anti-clotting agents, and immunosuppressive drugs.
Antibiotics may affect the quality of the blood and increase the risk of bacterial contamination, while anti-platelet and anti-clotting agents may increase the risk of bleeding in the recipient. Immunosuppressive drugs, on the other hand, may weaken the immune system of the recipient and make them vulnerable to infections.
Before donating blood, individuals are required to disclose any medications they are taking to the healthcare provider. This information is important to determine their eligibility to donate blood.
If the medication is deemed safe, the individual may be allowed to donate blood after a certain period of time has passed since their last dose. However, if the medication is deemed unsafe, the individual may be advised to wait until their treatment is completed or to seek an alternative medication.
It is important for individuals to be honest about their medication use when donating blood to ensure the safety of the recipient.
Lifestyle Factors That May Affect Eligibility
Factors such as tobacco use, alcohol consumption, and travel history to certain countries may impact an individual’s ability to donate blood.
Tobacco use, particularly smoking, can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases and impair the immune system.
Alcohol consumption, on the other hand, can affect liver function and lead to anemia, both of which may disqualify a person from donating blood.
Travel history to certain countries may also pose a risk for the transmission of infectious diseases, such as malaria and Zika virus, which can be transmitted through blood transfusions. Therefore, individuals who have recently traveled to areas where these diseases are endemic may be temporarily deferred from donating blood.
Other lifestyle factors that may affect eligibility for blood donation include body weight and physical activity level. A person’s weight and activity level can affect their hemoglobin levels, which may impact their ability to donate blood.
Additionally, individuals who engage in high-risk behaviors, such as intravenous drug use or unprotected sex, may also be ineligible to donate blood due to the risk of transmitting infectious diseases.
It is important to note that these factors do not automatically disqualify individuals from donating blood, but rather may require a temporary deferral or further evaluation by a healthcare professional before being cleared for donation.
Travel Restrictions for Blood Donation
Travel restrictions are implemented in blood donation centers to prevent the transmission of infectious diseases that may be prevalent in certain countries. These restrictions are in place to ensure the safety of both the donors and the recipients of blood transfusions. Countries that have a high prevalence of infectious diseases such as malaria, HIV, and hepatitis B and C are often subject to travel restrictions.
The length of travel restrictions may vary depending on the specific infectious disease and the country in question. For example, individuals who have traveled to areas with a high risk of malaria may be temporarily deferred from donating blood for up to 12 months after leaving the area. Similarly, those who have traveled to areas with a high risk of HIV may be deferred from donating blood for a period of time ranging from three months to indefinitely, depending on the duration of their stay and other factors.
Potential donors should always disclose their travel history to blood donation centers to determine their eligibility.
Screening Process for Donors
The screening process for potential blood donors is a vital step in ensuring the safety and effectiveness of blood transfusions. The process involves several steps, including a pre-donation questionnaire, a physical examination, and laboratory testing of the donated blood.
Donors are required to provide accurate information about their medical history, including any medications they are currently taking and any recent illnesses or surgeries. The physical examination includes a check of the donor’s blood pressure, pulse, and temperature, as well as an examination of the veins in the donor’s arm to ensure they are suitable for donation.
Laboratory testing of the donated blood is done to detect any infectious agents that may be present, such as viruses or bacteria, that could be transmitted to the recipient.
Once the screening process has been completed, donors who meet the eligibility criteria are allowed to donate blood. However, even after the screening process, there is still a small risk that infectious agents may be present in the donated blood.
To minimize this risk, blood banks and transfusion services use several additional safety measures, including testing the donated blood for infectious agents, processing the blood to remove any potentially harmful components, and storing the blood in a way that prevents contamination. By taking these steps, blood banks and transfusion services can ensure that donated blood is safe and effective, and that it can be used to save the lives of patients who need it.
Ensuring the Safety and Reliability of the Blood Supply
After undergoing the screening process, blood donors who meet the eligibility criteria can donate blood. But the responsibility of ensuring the safety and reliability of the blood supply does not end with the screening process alone.
It involves several measures and protocols to be implemented by blood banks and transfusion services to minimize the risks associated with blood transfusion. One of the critical measures is the implementation of standard operating procedures for the collection, testing, and distribution of blood and blood components. These procedures aim to minimize the risk of contamination, errors, and adverse reactions during the transfusion process.
Moreover, blood banks and transfusion services must adhere to regulatory guidelines and quality standards to ensure that the blood supply is safe and reliable. This involves regular inspection and monitoring of their facilities and practices by regulatory authorities and accreditation bodies.
By following these protocols and guidelines, blood banks and transfusion services can provide safe and reliable blood supply to patients in need.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blood donation is a crucial process that can save countless lives. However, not everyone is eligible to donate blood due to various health, lifestyle, and travel-related factors.
Age and weight requirements, as well as health conditions and medications, can all affect eligibility. Additionally, lifestyle choices such as engaging in high-risk behaviors can disqualify potential donors.
To ensure the safety and reliability of the blood supply, a stringent screening process is in place to identify any potential risks. Donors are asked about their medical history, travel history, and lifestyle choices, and their blood is tested for infectious diseases before being used for transfusions.
By following these guidelines and restrictions, blood donation can continue to be a safe and effective way to save lives. It is important for individuals who are interested in donating blood to familiarize themselves with the eligibility requirements and to consult with their healthcare provider if they have any questions or concerns.