Sensory System Processing Disorders And Perception
Sensory system processing disorders refer to a range of conditions in which individuals experience difficulties in processing and responding to sensory information from their environment. These disorders can affect the way individuals perceive and respond to various sensory stimuli, including touch, sound, taste, smell, and sight.
Sensory processing disorders can affect individuals of all ages and can have a significant impact on their daily lives, including their ability to interact with others, engage in recreational activities, and perform everyday tasks.
While the exact causes of sensory system processing disorders remain unclear, researchers believe that they may arise from a combination of genetic, environmental, and developmental factors. Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to sensory processing disorders, while others may develop these conditions as a result of exposure to certain environmental triggers, such as toxins, infections, or trauma.
Understanding the different types of sensory processing disorders, as well as their symptoms, can help individuals and their families better manage these conditions and improve their quality of life.
Key Takeaways
- Sensory system processing disorders affect how individuals process and respond to sensory information from their environment, and can impact daily life, including social interactions and performing everyday tasks.
- The causes of sensory system processing disorders are not fully understood but may be related to genetics, environment, and development, and early identification and intervention are crucial to managing these disorders.
- There are several types of sensory system processing disorders, including auditory, visual, tactile, vestibular, and proprioceptive processing disorders, and sensory overresponsivity, sensory underresponsivity, and sensory seeking are types of sensory processing disorders.
- Sensory integration therapy, occupational therapy, and other interventions can help regulate sensory needs and enhance daily functioning, and coping strategies such as deep pressure touch, sensory breaks, and sensory diets can significantly improve an individual’s quality of life and increase their ability to participate in daily activities.
Understanding Sensory System Processing Disorders
An in-depth understanding of sensory system processing disorders is essential to identifying and treating sensory perception issues in individuals.
Sensory system processing disorders, also known as sensory processing disorders (SPD), are conditions that affect the way the brain processes and responds to sensory input.
Individuals with SPD may have difficulty processing information received through their senses, such as touch, sound, taste, smell, and sight.
They may experience hypersensitivity (over-responsiveness) or hyposensitivity (under-responsiveness) to sensory stimuli, leading to anxiety, disorientation, and difficulty with coordination and social interactions.
SPD can affect individuals of any age, but it is commonly diagnosed in children.
It is estimated that 5-16% of children have SPD, and it often co-occurs with other developmental disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
The exact causes of SPD are not fully understood, but it is thought to be related to differences in brain function and neural connectivity.
Early identification and intervention are crucial to managing SPD and improving the individual’s quality of life.
Treatment strategies may involve sensory integration therapy, occupational therapy, and behavioral and cognitive therapies that aim to improve sensory processing abilities and enhance adaptive skills.
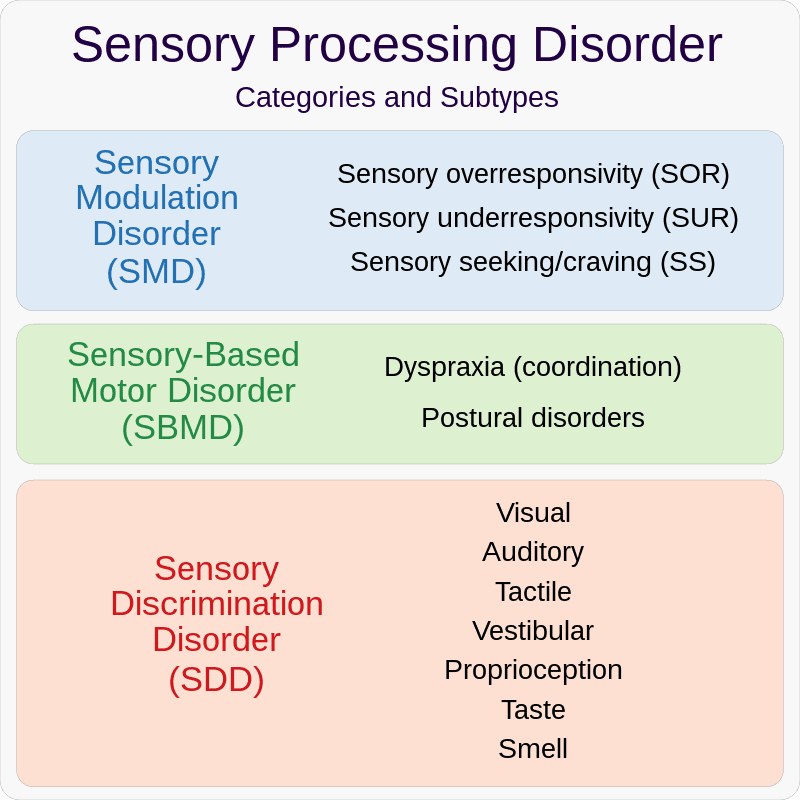
Types of Sensory System Processing Disorders
Classification of atypical sensory responses is crucial in understanding the underlying mechanisms of sensory processing difficulties. There are several types of sensory system processing disorders, and each type involves different sensory systems. These disorders can affect individuals of all ages, genders, and races, and their symptoms can range from mild to severe. The following table provides an overview of the types of sensory system processing disorders, their sensory systems affected, and their typical symptoms.
| Type of Disorder | Sensory System(s) Affected | Typical Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Auditory Processing Disorder | Auditory | Difficulty processing and interpreting auditory information, such as difficulty understanding speech in noisy environments |
| Visual Processing Disorder | Visual | Difficulty processing and interpreting visual information, such as difficulty reading or understanding visual images |
| Tactile Processing Disorder | Tactile | Difficulty processing and interpreting touch sensations, such as discomfort with certain textures or clothing |
| Vestibular Processing Disorder | Vestibular | Difficulty processing and interpreting information related to balance and movement, such as difficulty with coordination or motion sickness |
| Proprioceptive Processing Disorder | Proprioceptive | Difficulty processing and interpreting information related to body position and movement, such as difficulty with fine motor skills or spatial awareness |
It is important to note that individuals can have multiple types of sensory system processing disorders simultaneously, and that symptoms can vary from person to person. A thorough evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional is necessary to accurately diagnose and treat these disorders.
Sensory Overresponsivity
Individuals with heightened sensitivity to sensory input may experience an overresponsivity that can significantly impact their daily functioning. This condition, known as sensory overresponsivity (SOR), is characterized by an extreme reaction to sensory stimuli that are typically tolerated by most people. The individual may experience discomfort, pain, or anxiety in response to stimuli such as sounds, lights, textures, tastes, or smells.
SOR is often observed in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), but it can also occur in individuals without any other developmental or neurological condition. The symptoms of SOR can vary depending on the individual and the type of stimuli, but they typically involve an exaggerated or inappropriate response to sensory input.
For example, an individual with SOR may find the sound of a vacuum cleaner intolerable, or they may refuse to wear certain clothing because of the texture. These reactions can significantly impact an individual’s daily activities and quality of life, making it difficult to participate in social events, attend school or work, or engage in other routine activities.
Sensory Underresponsivity
The phenomenon of sensory underresponsivity relates to a reduced reaction or lack of response to sensory stimuli, which can hinder an individual’s ability to process and engage with their environment. This condition can affect multiple sensory modalities, including touch, taste, smell, sight, and hearing.
Individuals with sensory underresponsivity may not pay attention to sensory information, fail to respond to stimuli, or take longer than usual to react. This can result in difficulties with communication, social interaction, and learning.
Here are five examples of how sensory underresponsivity can manifest:
- A child may not respond to their name being called, even when others nearby do.
- An individual may not notice a change in the temperature of a room, such as when the AC turns on or off.
- Someone may not feel pain or discomfort from an injury, leading to delayed or inadequate medical attention.
- A person may not respond to visual cues, such as not noticing a sign or gesture.
- Someone may not notice or react to a sound, such as a phone ringing or an alarm going off.
It is important to note that sensory underresponsivity is not the same as intentional ignoring or lack of attention. It is a neurological difference in how the brain processes and responds to sensory information.
Addressing sensory underresponsivity may involve sensory integration therapy, occupational therapy, and other interventions to improve sensory processing and enhance daily functioning.
Sensory Seeking
One possible cause of atypical behavior in response to sensory stimuli is an imbalance in the regulation of arousal levels.
Sensory seeking is a type of sensory processing disorder that is characterized by an excessive need for stimulation. Individuals with this disorder actively seek out sensory experiences that are intense and often engage in risky behavior.
They may enjoy activities such as spinning, jumping, or climbing, or have a fascination with bright lights or loud noises. Sensory seeking behavior can have a significant impact on an individual’s daily life, as it can interfere with their ability to learn, interact with others, and engage in appropriate social behavior.
It can also be a sign of other underlying neurological conditions such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) or autism spectrum disorder (ASD). It is important for individuals who exhibit sensory seeking behavior to receive a proper diagnosis and treatment plan, which may include sensory integration therapy, occupational therapy, or other forms of intervention to help regulate their sensory needs.
Sensory Discrimination Disorder
Symptoms of sensory discrimination disorder can include difficulty distinguishing between different textures, tastes, or smells, which can impact an individual’s ability to perform daily tasks such as cooking or self-care.
Sensory discrimination disorder is a neurological condition that affects the way an individual processes sensory information. It can affect any of the senses, including touch, taste, smell, sight, and hearing.
Individuals with sensory discrimination disorder may have difficulty identifying subtle differences in sensory input, such as the flavor of different foods or the texture of clothing.
Sensory discrimination disorder can have a significant impact on an individual’s daily life. For example, an individual may have difficulty identifying the different ingredients in a recipe, making it challenging to cook or bake. Similarly, they may have trouble distinguishing between different fabrics, making it difficult to choose clothing that is comfortable or appropriate for different situations.
Other symptoms of sensory discrimination disorder can include sensitivity to certain textures or smells, as well as difficulty with fine motor tasks such as tying shoelaces or buttoning clothing.
Treatment for sensory discrimination disorder typically involves working with an occupational therapist to develop strategies for managing symptoms and improving sensory processing abilities.
Sensory Modulation Disorder
Individuals with sensory modulation disorder may experience difficulties regulating their responses to sensory input, leading to either over- or under-responsiveness to stimuli. This disorder affects how the nervous system processes and interprets sensory information, such as touch, taste, smell, sound, and sight. As a result, individuals with this disorder may find it challenging to adapt to new environments or activities that expose them to different sensory stimuli.
There are three main types of sensory modulation disorder: sensory seeking, sensory avoiding, and sensory sensitivity. Sensory seeking individuals crave intense sensory input, such as loud music or bright lights. They may engage in self-stimulatory behaviors, such as rocking or spinning.
Sensory avoiding individuals, on the other hand, are hypersensitive to sensory input and may find certain stimuli overwhelming. They may try to avoid situations or activities that expose them to these stimuli.
Finally, individuals with sensory sensitivity may have difficulty processing and integrating sensory information, leading to either over- or under-responsiveness to stimuli. They may be easily distracted or overwhelmed by sensory input or may not respond to it at all.
Understanding the different types of sensory modulation disorder can help professionals tailor interventions to the individual’s specific needs.
Coping Strategies for Sensory System Processing Disorders
Effective coping strategies for managing difficulties related to sensory modulation can significantly improve an individual’s quality of life and increase their ability to participate in daily activities. Sensory system processing disorders can be overwhelming, and for individuals experiencing them, the world can be a constant source of discomfort and stress. However, there are several coping strategies that can help reduce sensory overload and improve one’s ability to manage their sensory experiences.
One such strategy is deep pressure touch, which involves applying pressure to the body through activities such as weighted blankets or vests. This can help individuals feel more grounded and reduce feelings of anxiety. Another helpful strategy is sensory breaks, which involve taking short breaks throughout the day to engage in calming activities such as deep breathing, stretching, or listening to music. Finally, sensory diets can be developed with the help of an occupational therapist, which involve incorporating specific sensory activities into one’s daily routine to help regulate their sensory experiences. These coping strategies can be effective in managing sensory system processing disorders and improving an individual’s ability to participate in daily activities.
| Coping Strategy | Description | Benefits | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deep Pressure Touch | Applying pressure to the body through activities such as weighted blankets or vests | Can help individuals feel more grounded and reduce feelings of anxiety | ||
| Sensory Breaks | Taking short breaks throughout the day to engage in calming activities such as deep breathing, stretching, or listening to music | Can help individuals regulate their sensory experiences | ||
| Sensory Diets | Developing specific sensory activities into one’s daily routine with the help of an occupational therapist | Can help individuals manage sensory experiences and improve daily functioning | This can include activities such as brushing the skin with a soft brush, using a weighted blanket, or incorporating movement breaks throughout the day. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, sensory system processing disorders are a complex and varied set of conditions that can have a significant impact on an individual’s perception of their environment. Understanding the different types of disorders, including sensory overresponsivity, sensory underresponsivity, sensory seeking, sensory discrimination disorder, and sensory modulation disorder, can help to identify and provide appropriate interventions for those who may be struggling with these conditions.
Coping strategies for sensory system processing disorders can also be helpful in managing symptoms and improving function. These strategies may include sensory diets, sensory integration therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and other forms of support and accommodations.
While there is still much to learn about these disorders, continued research and awareness can help to improve outcomes and quality of life for individuals living with sensory system processing disorders.